Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Efavirenz (Efavirenzum)
Graphic formula.
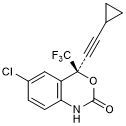
Molecular formula. C14H9ClF3NO2
Relative molecular mass. 315.7
Chemical name. (4S)-6-chloro-4-(cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (IUPAC).
CAS Registration Number. 154598-52-4
Description. White to slightly pink powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water R, freely soluble in methanol R.
Category. Antiretroviral (non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor).
Storage. Efavirenz should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Efavirenz may exhibit polymorphism.
Requirements
Definition. Efavirenz contains not less than 97.0% and not more than 102.0% of C14H9ClF3NO2, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity test
-
Either tests A and E, or any two of tests B, C and D, together with test E, may be applied.
-
Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from efavirenz RS or with the reference spectrum of efavirenz.
If the spectra thus obtained are not concordant, repeat the test using the residues obtained by separately dissolving the test substance and efavirenz RS in a small amount of methanol R and evaporating to dryness. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from efavirenz RS.
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions and solution (1) given under "Related substances, procedure 1". For solution (2), dissolve 12.5 mg efavirenz RS in 25.0 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R. Inject 35 µL each of solutions (1) and (2). Record the UV spectra of the peaks due to efavirenz in the chromatograms with a diode array detector in the range of 210 nm to 400 nm. The retention time and the UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time and the UV spectrum of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography , using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 90 volumes of dichloromethane R, 10 volumes of methanol R and 3 volumes of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μL of each of the two solutions in methanol R containing (A) 5 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 5 mg of efavirenz RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry exhaustively in air or in a current of cool air. Examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot obtained with solution (A) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity to that obtained with solution (B).
-
Prepare the test solution as described under "Assay". The absorption spectrum (1.6) of the final solution, when observed between 210 nm and 300 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 247 nm.
Alternatively, and in combination with identity test B, where a diode array detector is available, record the UV spectra of the principal peaks in the chromatograms with a diode array detector in the range of 210 nm to 300 nm. The UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the UV spectrum of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2)
-
Carry out test E.1 or, where HPLC and the indicated chiral columns are available, test E.2.
E.1 Determine the specific optical rotation (1.4) of a 3.0 mg/mL solution in methanol R and calculate with reference to the dried substance;
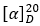 = -89 to -100.
= -89 to -100.E.2 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions and solution (1) given under "Impurity K (efavirenz enantiomer)". For solution (2), dissolve 10 mg efavirenz RS in 50.0 mL mobile phase. Inject 20 µL each of solutions (1) and (2). The retention time of the principal peak obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
Sulfated ash (2.3). Use a platinum crucible, not more than 2.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry for 4 hours at 105 °C; it loses not more than 5 mg/g.
Impurity K (efavirenz enantiomer). Prepare fresh solutions and perform the tests without delay. Protect solutions from light.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (15 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded amylose tris(3,5-dimethylphenylcarbamate) (5 µm). As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 980 volumes of hexane R, 20 volumes of ethanol R and 2 volumes of diethylamine R.
Operate at a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 252 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 25 °C.
Prepare the following solutions in mobile phase. For solution (1), dissolve 20 mg of the test substance in 100.0 mL. For solution (2), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL. For solution (4), prepare a solution as described in the leaflet of racemic efavirenz RS to contain 0.1 mg of racemic efavirenz RS per mL.
Inject 20 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (3) and (4).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) to identify the peaks due to efavirenz and impurity K. Impurity K is eluted with a relative retention of about 1.8 with reference to efavirenz (retention time about 9.3 minutes).
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4), the resolution between the peaks due to efavirenz and impurity K is at least 5.0. Also, the test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak due to efavirenz is detected with a signal-to-noise ratio of at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity K is not greater than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%).
Related substances
Procedure 1. Prepare fresh solutions and perform the tests without delay. Protect solutions from light and use polypropylene HPLC vials to avoid possible degradation in certain types of glass vials.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (15 cm x 4.6 mm), packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded cyanopropyl groups (5 μm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
- mobile phase A: a mixture of methanol R, trifluoroacetic acid R and water R (100:0.5:900 V/V/V) (Note: use only freshly-opened trifluoroacetic acid – opened not longer than 6 months);
-
mobile phase B: a mixture of methanol R, trifluoroacetic acid R and water R (900: 0.5:100 V/V/V) (Note: use only freshly-opened trifluoroacetic acid – opened not longer than 6 months).
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Comments |
|
0–16 |
60 to 50 |
40 to 50 |
Linear gradient |
|
16–23 |
50 to 35 |
50 to 65 |
Linear gradient |
|
23–28 |
35 to 30 |
65 to 70 |
Linear gradient |
|
28–29 |
30 to 20 |
70 to 80 |
Linear gradient |
|
29–31 |
20 |
80 |
Isocratic |
|
31–32 |
20 to 60 |
80 to 40 |
Return to initial composition |
|
32–40 |
60 |
40 |
Re-equilibration |
Prepare the following solutions in a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R.
For solution (1), dissolve 25 mg of the test substance and dilute to 50.0 mL. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL. For solution (2) dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (2) to 20.0 mL. For solution (4), dissolve 1 mg of efavirenz impurity B RS in 10 mL. Dilute 1 mL of the resulting solution to 25 mL. For solution (5), dissolve 1 mg of efavirenz RS in 10 mL of solution (4). For solution (6) dissolve 10 mg of the test substance in 20 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of methanol R and water R. Add 2 mL of sodium hydroxide (~4 g/L) TS and heat in a stoppered vial at about 80 °C for 2 hours. Cool to room temperature and dilute 1 mL of this solution to 10 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R.
Operate at a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 250 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 40 °C.
Inject 35 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (3), (5) and (6).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (5) to identify the peak due to impurity B and the chromatogram obtained with solution (6) to identify the peaks due to impurity E, impurity F and impurity H.
The impurities, if present, are eluted at the following relative retentions with reference to efavirenz (retention time about 13 minutes): impurity J about 0.19; impurity E about 0.51; impurity B about 0.93; impurity Q about 1.16; impurity R about 1.16; impurity S about 1.16; impurity C about 1.20; impurity G about 1.28; impurity H about 1.33, impurity F about 1.50; impurity L about 1.53; impurity M about 1.60; impurity N about 1.63; impurity I about 1.75; impurity D about 1.80; impurity A about 1.90; impurity O about 2.10; impurity P about 2.18.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5), the resolution between the peaks due to impurity B and efavirenz is at least 1.2. Also, the test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak due to efavirenz is obtained with a signal-to-noise ratio of at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B is not greater than 0.4 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogramobtained with solution (2) (0.4 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity D, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.4, is not greater than 0.25 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.25 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.8, is not greater than 0.15 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity C is not greater than 0.15 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity E, when multiplied by a correction factor of 3.8, is not greater than 0.15 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity F, when multiplied by a correction factor of 0.5, is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity N, when multiplied by a correction factor of 3.0, is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity P, when multiplied by a correction factor of 2.1, is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %); and
-
the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10%).
-
The sum of the areas of all impurity peaks, including the corrected areas of any peaks corresponding to impurities A, D, E, F, N and P, is not greater than the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.05 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Perform procedure 2 if the sum of the areas of the peaks corresponding to impurities Q, R and S, all with a relative retention of 1.16, is greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to efavirenz in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10%).
Procedure 2 (impurities Q, R and S). Prepare fresh solutions and perform the tests without delay. Protect solutions from light.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm), packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 μm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
-
mobile phase A: a mixture of acetonitrile R, trifluoroacetic acid R and water R (400:0.5:600 (V/V/V)(Note: use only freshly-opened trifluoroacetic acid – opened not longer than 6 months);
-
mobile phase B: a mixture of acetonitrile R, trifluoroacetic acid R and water R (800:0.5:200 (V/V/V)) (Note: use only freshly-opened trifluoroacetic acid – opened not longer than 6 months).
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Comments |
|
0–40 |
100 to 0 |
0 to 100 |
Linear gradient |
|
40–45 |
0 |
100 |
Isocratic |
|
45–46 |
0 to 100 |
100 to 0 |
Return to initial composition |
|
46–50 |
100 |
0 |
Re-equilibration |
Prepare the following solutions using a mixture of acetonitrile R, trifluoroacetic acid R and water (55:0.05:45, V/V/V) as diluent.
For solution (1), dissolve 25 mg of the test substance and dilute to 50.0 mL. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL. For solution (2), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 20.0 mL.
Operate at a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 250 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 35 °C.
Inject 20 µL each of solutions (1) and (2).
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak due to efavirenz is obtained with a signal-to-noise ratio of at least 10.
The impurities, if present, are eluted at the following relative retentions with reference to efavirenz (retention time about 17 minutes): impurity Q about 1.10, impurity R about 1.13 and impurity S about 1.14.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the areas of any peaks corresponding to impurities Q, R or S are each not greater than 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10%).
Assay
- Either test A or test B may be applied.
-
Dissolve about 25.0 mg of the test substance in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Measure the absorbance (1.6) of the resulting solution in a cuvette or cell with an optical pathlength of 10 mm at the maximum at about 247 nm. Calculate the amount of efavirenz (C14H9CIF3NO2) using an absorptivity value of 55.0 (
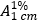 = 550).
= 550).[Note from the Secretariat. The value for the absorptivity will be confirmed during the establishment of efavirenz ICRS.]
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions given below under "Related Substances", Procedure 1, with the following modifications:
Prepare the following solutions in a mixture of equal volumes of acetonitrile R and water R.
For solution (1), dissolve 50.0 mg of the test substance and dilute to 100.0 mL. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL.
For solution (2), dissolve 50.0 mg of efavirenz RS and dilute to 100.0 mL. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL.
Inject 20 μL each of solutions (1) and (2) and record the chromatograms.
Measure the areas of the peaks corresponding to efavirenz obtained in the chromatograms of solutions (1) and (2) and calculate the percentage content of efavirenz (C14H9ClF3NO2) with reference to the dried substance, using the declared content of C14H9ClF3NO2 in efavirenz RS.
Impurities
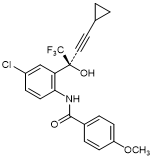
A. N-{4-Chloro-2-[(2S)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-hydroxybut-3-yn-2-yl]phenyl}-4-methoxybenzamide (synthesis-related product),
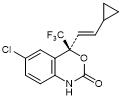
B. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-[(E)-2-cyclopropylethenyl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one;
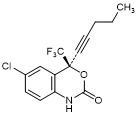
C. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-(pent-1-yn-1-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one;
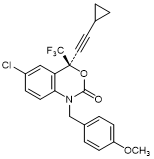
D. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-(cyclopropylethynyl)-1-[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one;
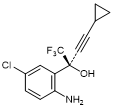
E. (2S)-2-(2-Amino-5-chlorophenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluorobut-3-yn-2-ol;
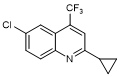
F. 6-Chloro-2-cyclopropyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)quinoline; quinoline analogue (synthesis-related product and degradation product);
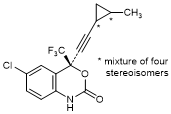
G. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-[2-(2-methylcyclopropyl)ethynyl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (mixture of four stereoisomers);
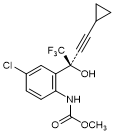
H. Methyl {4-chloro-2-[(2S)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-hydroxybut-3-yn-1-yl]phenyl}carbamate;
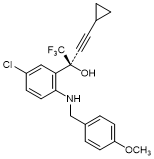
I. (2S)-2-(5-Chloro-2-{[(4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]amino}phenyl)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluorobut-3-yn-2-ol (synthesis-related product);
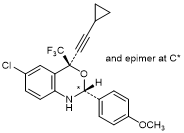
J. (2RS,4S)-6-Chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazine (synthesis-related product),
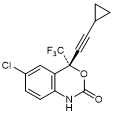
K. (4R)-6-Chloro-4-(2-cyclopropylethynyl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (efavirenz enantiomer) (synthesis-related impurity),
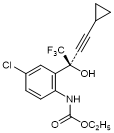
L. Ethyl {4-chloro-2-[(2S)-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-hydroxybut-3-yn-2-yl]phenyl}carbamate; efavirenz amino alcohol ethyl carbamate (synthesis-related product),
M. Unknown impurity,
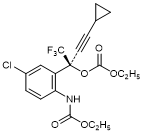
N. (2S)-2-{5-Chloro-2-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl}-4-cyclopropyl-1,1,1-trifluorobut-3-yn-2-yl ethyl carbonate; efavirenz amino alcohol bis(ethoxycarbonyl) (synthesis-related product),
O. Unknown impurity,
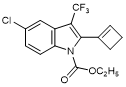
P. Ethyl 5-chloro-2-(cyclobut-1-en-1-yl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-indole-1-carboxylate; cyclobutenylindole analogue (synthesis-related product),
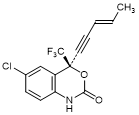
Q. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-[(3E)-pent-3-en-1-yn-1-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (trans) (synthesis-related product),
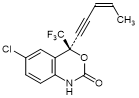
R. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-[(3Z)-pent-3-en-1-yn-1-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one (cis) (synthesis-related product),
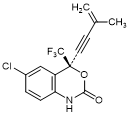
S. (4S)-6-Chloro-4-(3-methylbut-3-en-1-yn-1-yl)-4-(trifluoromethyl)-1,4-dihydro-2H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-one; efavirenz penteneyne (synthesis-related product).