Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Ergocalciferol (Ergocalciferolum)
Molecular formula. C28H44O
Relative molecular mass. 396.7
Graphic formula.
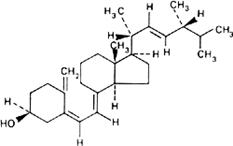
Chemical name. (5Z,7E,22E)-9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10(19),22-tetraene-3β-ol; 24-methyl-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10( 19),22-tetraene-3β-ol; CAS Reg. No. 50-14-6.
Other name. Vitamin D2.
Description. Colourless or slightly yellowish crystals or a white or slightly yellowish, crystalline powder; odourless or almost odourless.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, acetone R and ether R.
Category. Vitamin, antirachitic.
Storage. Ergocalciferol should be kept in a hermetically closed container, preferably in an inert atmosphere, such as nitrogen, protected from light and stored at a temperature between 2 and 8 °C.
Additional information. Ergocalciferol is affected by air and by light. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Ergocalciferol contains not less than 95.0% and not more than 105.0% of C28H44O.
Identity tests
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from ergocalciferol RS or with the reference spectrum of ergocalciferol.
B. Dissolve about 2 mg in 10 mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS. To 1.0 mL add carefully 5 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS and mix; a red colour is produced (distinction from colecalciferol, which gives a yellow colour).
C. Dissolve 5 mg in 5 mL of chloroform R, add about 0.5 mL of acetic anhydride R and about 0.1 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS, shake well; the colour of the solution changes immediately from red to violet, then to blue, and finally to dark green.
D. Dissolve about 1 mg in 40 mL of dichloroethane R. To 1 mL of this solution add 4 mL of antimony trichloride TS; an orange colour is produced, which gradually becomes pink.
Melting range. 112-117°C, determined without previous grinding or drying.
Specific optical rotation. Dissolve 0.2 g rapidly and without heating in sufficient aldehyde-free ethanol (~750 g/l) TS to produce 25 mL. Determine the rotation within 30 minutes of preparation; 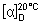 = +103° to +107°.
= +103° to +107°.
Ergosterol. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R1 as the coating substance, and as the mobile phase use a mixture of equal volumes of cyclohexane R and peroxide-free ether R, the mixture containing 0.10 mg of butylated hydroxytoluene R per mL. Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of the following solutions prepared immediately before use in a mixture of dichloroethane R containing 10 mg of squalane R and 0.10 mg of butylated hydroxytoluene R per mL: (A) 0.050 g of the test substance per mL, (B) 0.050 g of ergocalciferol RS per mL, (C) 0.10 mg of ergosterol R per mL; also apply to the plate 20 μl of solution (D) consisting of a mixture of equal volumes of solutions B and C. Develop the plate at once in the dark. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and spray it three times with antimony trichloride TS. Wait after spraying 3-4 minutes, then examine the chromatogram in daylight. The principal spot obtained with solution A is initially orange-yellow and then becomes brown; it corresponds in position, appearance and intensity with that obtained with solution B. Any violet spot obtained with solution A with an Rf value slightly less than that of the principal spot is not more intense than the spot obtained with solution C. The chromatogram obtained with solution A shows no additional spots compared with the chromatograms obtained with solutions B and C. The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution D shows two clearly separated spots.
Reducing substances. Dissolve 0.10 g in 10 mL of aldehyde-free ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, add 0.5 mL of blue tetrazolium/ethanol TS and 0.5 mL of tetramethylammonium hydroxide/ethanol TS. Allow to stand for exactly 5 minutes and then add 1 mL of glacial acetic acid R. Measure the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 525 nm against a solvent cell containing a solution prepared by treating 10 mL of aldehyde-free ethanol (~750 g/l) TS in a similar manner. The absorbance is not greater than that obtained by repeating the operation with 10 mL of a solution containing 0.2 μg/mL of hydroquinone R in aldehyde-free ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Assay. Dissolve rapidly and without heating 0.05 g, accurately weighed, in sufficient aldehyde-free ethanol (~750 g/l) TS to produce 100 mL; dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 250 mL with the same solvent. Measure within 30 minutes of preparation the absorbance of a 1-cm layer of the diluted solution at the maximum at about 265 nm. Calculate the amount of C28H44O in the substance being examined by comparison with ergocalciferol RS, similarly and concurrently examined. In an adequately calibrated spectrophotometer the absorbance of the reference solution should be 0.48 ± 0.03.