Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Fluorouracil (Fluorouracilum)
Molecular formula. C4H3FN2O2
Relative molecular mass. 130.1
Graphic formula.
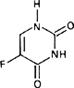
Chemical name. 5-Fluorouracil; 5-fluoro-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; CAS Reg. No. 51-21-8.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Sparingly soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Cytotoxic drug.
Storage. Fluorouracil should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Fluorouracil melts at about 282°C with decomposition. CAUTION: Fluorouracil must be handled with care, avoiding contact with the skin and inhalation of airborne particles.
Requirements
Definition. Fluorouracil contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.0% of C4H3FN2O2, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either test A alone or tests B, C and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from fluorouracil RS or with the reference spectrum of fluorouracil.
B. The absorption spectrum of a 10 μg/mL solution in acetate buffer, pH 4.7, TS, when observed between 220 nm and 350 nm, is qualitatively similar to that of a 10.0 μg/mL solution of fluorouracil RS in acetate buffer, pH 4.7, TS (a maximum occurs at about 266 nm and a minimum occurs at about 232 nm). The absorbances of the solutions at the maximum do not differ from each other by more than 3%. The absorbance of a 1-cm layer at 266 nm is about 0.54.
C. Heat 0.5 mL of chromic acid TS in a small test-tube in a water-bath for 5 minutes; the solution wets the sides of the tube but there is no greasiness. Add about 3 mg of the test substance arid again heat in a water-bath for 5 minutes; the solution no longer wets the sides of the tube.
D. Dissolve 0.05 g in 5 mL of water, add 1 mL of bromine TS1; the colour of the bromine is discharged.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry at 80 °C under reduced pressure (not exceeding 0.6 kPa or about 5 mm of mercury) over phosphorus pentoxide R for 4 hours; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance (a precoated plate from a commercial source is suitable) and a mixture of 70 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 15 volumes of methanol R, and 15 volumes of water as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of 2 solutions in a mixture of equal volumes of water and methanol R containing (A) 20 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.050 mg of fluorouracil RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm). Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Fluorine content. Carry out the combustion as described under 2.4 Oxygen flask method, using 7 mg of the test substance, and adding about 15 mg of sodium peroxide R and 15 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS as the absorbing liquid. When the process is complete, allow the flask to stand for not less than 10 minutes with intermittent shaking, then dilute the contents to 100 mL with water. Proceed with 5.0 mL as described under 2.4 Oxygen flask method for the determination of fluorine; not more than 55 μg of F.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.4 g, accurately weighed, in 80 mL of dimethylformamide R, add 0.25 mL of thymol blue/dimethylformamide TS and titrate with tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS to a blue end-point as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method B. Each mL of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 13.01 mg of C4H3FN2O2.
Additional requirements for Fluorouracil for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 0.33 IU of endotoxin RS per mg.