Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Fluphenazine hydrochloride (Fluphenazini hydrochloridum)
Molecular formula. C22H26F3N3OS,2HCl
Relative molecular mass. 510.4
Graphic formula.
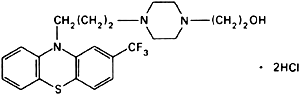
Chemical name. 4-[3-[2-(Trifluoromethyl)phenothiazin-10-yl]propyl]-1-piperazineethanol dihydrochloride; 4-[3-[2-(trifluoromethyl)-10H-phenothiazin-10-yl]propyl]-1-piperazineethanol dihydrochloride; CAS Reg. No. 146-56-5.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Soluble in 10 parts of water; sparingly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Neuroleptic.
Storage. Fluphenazine hydrochloride should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Even in the absence of light, Fluphenazine hydrochloride is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Fluphenazine hydrochloride contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.5% of C22H26F3N3OS,2HCl, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from fluphenazine hydrochloride RS or with the reference spectrum of fluphenazine hydrochloride.
B. Carry out the test in subdued light as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using kieselguhr R1 as the coating substance and a mixture of 15 volumes of formamide R, 5 volumes of 2-phenoxyethanol R, and 180 volumes of acetone R to impregnate the plate, dipping it about 5 mm beneath the surface of the liquid. After the solvent has reached the top of the plate, remove the plate from the chromatographic chamber and allow to stand at room temperature until the solvents have completely evaporated. Use the impregnated plate immediately, carrying out the chromatography in the same direction as the impregnation. As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 2 volumes of diethylamine R and 100 volumes of light petroleum R1 saturated with 2-phenoxyethanol R. Apply separately to the plate 2 μl of each of 2 solutions in chloroform R containing (A) 2.0 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 2.0 mg of fluphenazine hydrochloride RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (365 nm), observing the fluorescence produced after about 2 minutes. Spray the plate with sulfuric acid/ethanol TS and examine the chromatogram in daylight. The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity with that obtained with solution B.
C. Dissolve 5 mg in 5 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS; an orange colour is produced which becomes brownish red on warming.
D. Heat 0.5 mL of chromic acid TS in a small test-tube in a water-bath for 5 minutes; the solution wets the sides of the tube but there is no greasiness. Add about 3 mg of the test substance and again heat in a water-bath for 5 minutes; the solution no longer wets the sides of the tube.
E. A 0.05 g/mL solution yields reaction B described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of chlorides.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 2.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R2 as the coating substance and a mixture of 80 volumes of acetone R, 30 volumes of cyclohexane R and 5 volumes of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of each of 2 solutions in sodium hydroxide/methanol TS containing (A) 10 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.10 mg of the test substance per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm). Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. In order to avoid overheating during the titration, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.220 g in a mixture of 10 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and 40 mL of acetic anhydride R. Carry out a potentiometric titration using perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 25.52 mg of C22H26F3N3OS,2HCl.