Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Gentamicin sulfate (Gentamicini sulfas)
Gentamicin sulfate (non-injectable)
Gentamicin sulfate, sterile
Graphic formula.
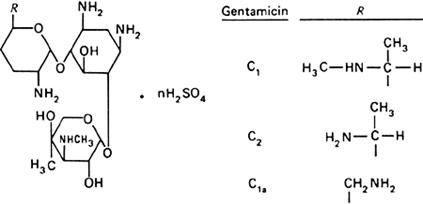
Chemical name. Gentamicin sulfate; CAS Reg. No. 1405-41-0.
Description. A white to cream-coloured powder; odourless.
Solubility. Soluble in water; practically insoluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and ether R.
Category. Antibacterial drug.
Storage. Gentamicin sulfate should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Labelling. The designation sterile Gentamicin sulfate indicates that the substance complies with the additional requirements for sterile Gentamicin sulfate and may be used for parenteral administration or for other sterile applications.
Additional information. Gentamicin sulfate is hygroscopic. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Gentamicin sulfate is the sulfate salt of gentamicin fractions C1, C2, and C1a produced by the growth of Micromonospora purpurea.
Gentamicin sulfate contains not less than 590 International Units of gentamicin per mg, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R5 as the coating substance (a precoated plate from a commercial source is suitable); shake together 1 volume of chloroform R, 1 volume of methanol R, and 1 volume of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, allow to separate and use the lower layer as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 1 μl of each of 2 solutions containing (A) 20 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 20 mg of gentamicin sulfate RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, spray it with triketohydrindene/pyridine/acetone TS, and heat it at 105°C for 2 minutes. Examine the chromatogram in daylight. The 3 principal spots obtained with solution A correspond with the 3 principal spots obtained with solution B.
B. A 10 mg/mL solution yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of sulfates.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 0.10 g/mL solution, and calculate with reference to the anhydrous substance: 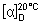 = +107° to +121°.
= +107° to +121°.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 10 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using about 0.2 g of the substance; the water content is not more than 150 mg/g.
pH value. pH of a 40 mg/mL solution, 3.5-5.5.
Assay. Carry out the assay as described under 3.1 Microbiological assay of antibiotics, using either Bacillus pumilus (NCTC 8241; ATCC 14884), Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6633), or Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538P) as the test organism, culture medium Cm1 with a final pH of 7.8, sterile phosphate buffer pH 8.0 TS1 or TS2, an appropriate concentration of gentamicin (usually between 2 and 20 IU per mL), and an incubation temperature of 35-39 °C. The precision of the assay is such that the fiducial limits of error of the estimated potency (P = 0.95) are not less than 95% and not more than 105% of the estimated potency. The upper fiducial limit of error of the estimated potency (P = 0.95) is not less than 590 IU per mg, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Additional Requirements for Gentamicin Sulfate for sterile use
Sterility. Complies with 3.2 Test for sterility.
Additional requirements for Gentamicin sulfate for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 1.70 IU of endotoxin RS per mg of gentamicin.