Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Glucose (Glucosum)
Glucose, anhydrous
Glucose monohydrate
Molecular formula. C6H12O6 (anhydrous); C6H12O6,H2O (monohydrate).
Relative molecular mass. 180.2 (anhydrous); 198.2 (monohydrate).
Graphic formula.
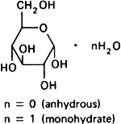
Chemical name. α-D-Glucopyranose; CAS Reg. No. 492-62-6 (anhydrous). α-D-Glucopyranose monohydrate; CAS Reg. No. 14431-43-7 (monohydrate).
Other name. Dextrose.
Description. Colourless crystals or a white, crystalline or granular powder; odourless.
Solubility. Soluble in about 1 part of water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; more soluble in boiling water and boiling ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Nutrient; fluid replenisher.
Storage. Glucose should be kept in a well-closed container.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Glucose should state whether the substance is the monohydrate or is in the anhydrous form. If the material is not intended for parenteral use a designation "for oral use only" should be added.
Additional information. Glucose has a sweet taste.
Requirements
Definition. Glucose contains not less than 99.0% and not more than 101.5% of C6H12O6, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
A. When heated it melts, swells up and burns, evolving an odour of burnt sugar.
B. Add a few drops of a 0.05 g/mL solution to 5 mL of hot potassio-cupric tartrate TS; a copious red precipitate is produced.
Specific optical rotation. Dissolve 10.0 g in 50 mL of water, add 0.2 mL of ammonia (~100 g/l) TS, and sufficient water to produce 100 mL, and allow to stand for 30 minutes. Calculate the result with reference to the anhydrous substance; 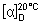 = +52.5° to +53.0°.
= +52.5° to +53.0°.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 1; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 5 μg/g.
Arsenic. Use a solution of 10 g in 35 mL of water and proceed as described under 2.2.5 Limit test for arsenic; not more than 1 μg/g.
Chlorides. Dissolve 1.25 g in a mixture of 2 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/l) TS and 20 mL of water, and proceed as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 0.2 mg/g.
Sulfates. Dissolve 2.5 g in 20 mL of water and proceed as described under 2.2.2 Limit test for sulfates; the sulfate content is not more than 0.2 mg/g.
Less-soluble sugars and dextrins. Boil 1 g with 30 mL of ethanol (~710 g/l) TS and cool; a clear solution is produced.
Soluble starch. Dissolve 2.5 g in 25 mL of water, boil the solution for 1 minute, cool and add 0.1 mL of iodine (0.1 mol/l) VS; no blue colour is produced.
Sulfites. Dissolve 2.5 g in 25 mL of water, add 0.1 mL of iodine (0.1 mol/l) VS and a few drops of starch TS; a blue colour is produced.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 5.0 g in 10 mL of water is clear and not more intensely coloured than standard colour solution Gn3 when compared as described under 1.11.1 Colour of liquids.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method. Method A. For the anhydrous form use about 1 g of the substance; the water content is not more than 10 mg/g. For the monohydrate use about 0.15 g of the substance; the water content is not less than 70 mg/g and not more than 95 mg/g.
Acidity. Dissolve 5.0 g in 50 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R and titrate with carbonate-free sodium hydroxide (0.02 mol/l) VS, using phenolphthalein/ethanol TS as indicator; not more than 0.5 mL is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (pink).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.10 g, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of water, add 25.0 mL of iodine (0.05 mol/l) VS and 10 mL of sodium carbonate (50 g/l) TS. Allow to stand for 20 minutes in the dark and add 15 mL of sulfuric acid (~100 g/l) TS. Titrate the excess of iodine with sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/l) VS, using starch TS as indicator. Repeat the operation without the substance being examined and make any necessary corrections. Each mL of iodine (0.05 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 9.008 mg of C6H12O6.
Additional requirements for Glucose for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 0.5 IU of endotoxin RS per mg.