Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Griseofulvin (Griseofulvinum)
Molecular formula. C17H17ClO6
Relative molecular mass. 352.8
Graphic formula.
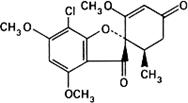
Chemical name. 7-Chloro-2',4,6-trimethoxy-6'β-methylspiro[benzofuran-2(3H),1'-[2]cyclohexene]-3,4'-dione; (1'S-trans)-7-chloro-2',4,6-trimethoxy-6'-methylspiro[benzofuran-2(3H),1'-[2]cyclohexene]-3,4'-dione; CAS Reg. No. 126-07-8.
Description. White to pale cream powder; almost odourless.
Solubility. Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; freely soluble in tetrachloroethane R.
Category. Antifungal.
Storage. Griseofulvin should be kept in a well-closed container.
Additional information. The particles of Griseofulvin are generally up to 5 μm in maximum dimension, although occasionally larger particles may be present that exceed 30 μm.
Requirements
Definition. Griseofulvin contains not less than 97.0% and not more than 102.0% of C17H17ClO6, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and D or tests B, C, and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from griseofulvin RS or with the reference spectrum of griseofulvin.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using kieselguhr R1 as the coating substance and a mixture of 1 volume of ethylmethylketone R and 1 volume of xylene R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of each of 2 solutions in chloroform R containing (A) 0.50 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.50 mg of griseofulvin RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm). The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity with that obtained with solution B.
C. Dissolve 5 mg in 1 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS and add 5 mg of powdered potassium dichromate R; a wine-red colour is produced.
D. Melting temperature, about 220°C.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 10 mg/mL solution in dimethylformamide R; 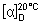 = +354° to +364°.
= +354° to +364°.
Particle size. In a mortar grind 10 mg with 10 drops of hydroxyethylcellulose TS, add a further 3.50 mL of hydroxyethylcellulose TS and grind again. Transfer a drop of the suspension to a suitable counting chamber 0.10 mm deep, place a cover glass over it, and examine under a microscope 10 fields of vision of 0.04 mm2 area each, using a magnification of 600×; not more than 30 crystals larger than 5 μm are visible in any field of vision.
Solution in dimethylformamide. A solution of 0.75 g in 10 mL of dimethylformamide R is clear and not more intensely coloured than standard colour solution Yw2 when compared as described under 1.11.1 Colour of liquids.
Matter soluble in light petroleum. Reflux 1.0 g with 40 mL of light petroleum R for 10 minutes, cool and filter. Wash the flask 3 times with 10 mL of light petroleum R, filter, evaporate the combined filtrates on a water-bath, and dry at 105°C for 1 hour; the weight of the residue does not exceed 2.0 mg.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 2.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
Acidity. Dissolve 0.25 g in 20 mL of neutralized ethanol TS and titrate with carbonate-free sodium hydroxide (0.02 mol/l) VS, phenolphthalein/ethanol TS being used as indicator; not more than 1.0 mL is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (pink).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.10 g, accurately weighed, in sufficient dehydrated ethanol R to produce 200 mL and dilute 2 mL of this solution to 100 mL with dehydrated ethanol R. Determine the absorbance of this solution in a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 291 nm and calculate the content of C17H17ClO6, using the absorptivity value of 68.6 (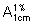 = 686).
= 686).