Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Hydrochlorothiazide (Hydrochlorothiazidum)
Molecular formula. C7H8ClN3O4S2
Relative molecular mass. 297.7
Graphic formula.
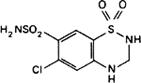
Chemical name. 6-Chloro-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,2,4-benzothiadiazine-7-sulfonamide 1,1-dioxide; CAS Reg. No. 58-93-5.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder; odourless or almost odourless.
Solubility. Very slightly soluble in water; practically insoluble in ether R; soluble in 200 parts of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and in 20 parts of acetone R.
Category. Diuretic.
Storage. Hydrochlorothiazide should be kept in a well-closed container.
Requirements
Definition. Hydrochlorothiazide contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C7H8ClN3O4S2, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from hydrochlorothiazide RS or with the reference spectrum of hydrochlorothiazide.
B. Mix 10 mg of the test substance and 10 mg of disodium chromotropate R, add 1 mL of water and, cautiously, 5 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS; a purple colour is produced.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 10 μg/g.
Free chlorides. For the preparation of the test solution shake 0.3 g with 20 mL of water and 10 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/l) TS for 5 minutes, and filter. Proceed with the filtrate as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 0.8 mg/g.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
Diazotizable substances. For the test solution place about 0.01 g, accurately weighed, in a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 10 mL of methanol R. Dilute to volume with water and mix.
For the reference solution weigh 5.0 mg of 4-amino-6-chloro-1,3-benzenedisulfonamide R, transfer to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in 1 mL of methanol R. Dilute to volume with water and mix. Dilute 4 mL of this solution with sufficient water to produce 100 mL (= 20 μg/mL).
Transfer 5 mL of the test solution and of the reference solution to separate 50-mL volumetric flasks, and 5 mL of water to a third 50-mL volumetric flask to serve as a blank. To each flask add 1 mL of freshly prepared sodium nitrite (10 g/l) TS and 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. Add 2 mL of ammonium sulfamate (25 g/l) TS, allow to stand for 5 minutes with frequent swirling, then add 2 mL of freshly prepared disodium chromotropate (10 g/l) TS and 10 mL of sodium acetate (150 g/l) TS. Dilute with water to volume and mix. Measure the absorbance at the maximum at about 500 nm, against the blank. The absorbance of the test solution does not exceed that of the reference solution (10 mg/g).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.3 g, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of pyridine R, add 5 drops of azo violet TS and titrate quickly with sodium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS to a deep blue end-point, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration. Method B. Each mL of sodium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 14.89 mg of C7H8ClN3O4S2.