Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide (Benzoylis peroxidum cum aqua)
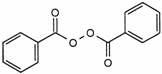
C14H10O4,xH2O
Relative molecular mass. 242.2 (anhydrous)
Chemical name. Dibenzoyl peroxide; CAS Reg. No. 94-36-0.
Description. A white, amorphous or granular powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; soluble in acetone R; soluble in dichloromethane R with separation of water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Keratolytic agent.
Storage. Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide should be kept in a container that has been treated to reduce static discharge and that has a device for the release of excess pressure. Store at a temperature between 2 and 8 °C, protected from light.
Additional information. CAUTION: Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide may explode at temperatures higher than 60 °C or if its water content is too low. It may burst into flame in the presence of reducing substances. Unused material must not be returned to the original container but destroyed by treating with sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS to a point where no iodine is liberated after acidifying with hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS and adding a crystal of potassium iodide R.
Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide loses water rapidly on exposure to air. It must be handled with care, avoiding contact with the skin and mucous membranes and inhalation of airborne particles.
Requirements
Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide contains not less than 70.0% and not more than 77.0% of C14H10O4, and not less than 20.0% of water.
Note: Before carrying out any tests, thoroughly mix the entire sample.
Identity tests
• Either test A alone or tests B, C, and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the reference spectrum of benzoyl peroxide.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R4 as the coating substance and a mixture of 50 volumes of toluene R, 2 volumes of dichloromethane R, and 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5ml of each of 2 solutions in methanol R containing (A) 10.0mg of Hydrous Benzoyl peroxide per mL, and (B) a solution of hydrous benzoyl peroxide R containing the equivalent of 10.0mg of benzoyl peroxide per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity with that obtained with solution B.
C. Dissolve about 25 mg in 2 mL of acetone R, add 1 mL of diethylphenylenediamine sulfate TS, and mix; a red colour is produced which turns rapidly to dark violet within 5 minutes.
D. To 1 g add 5 mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, 5ml of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS, and 10 mL of water. Boil the mixture under a reflux condenser for 20 minutes and cool. To 1ml of the resulting solution add 0.5 mL of ferric chloride (65 g/l) TS; a dull yellow precipitate is produced which is soluble in ether R.
Chlorides. Dissolve a quantity containing the equivalent of 0.5 g of anhydrous Benzoyl peroxide in 15 mL of acetone R. Add, while stirring, 50 mL of nitric acid (0.05 mol/l) VS, allow to stand for 10 minutes, and filter. Wash the residue with two quantities, each of 10 mL, of nitric acid (0.05 mol/l) VS, combining the filtrate and the washings. Dilute this solution to 100 mL with nitric acid (0.05 mol/l) VS. Using 2.5 mL of this solution, proceed as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content does not exceed 4 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using 5.0 mL of solution A as prepared below under "Assay". Add 3 mL of a solution containing 0.10 g of potassium iodide R in dimethylformamide R. Stir for 5 minutes before starting the titration. Repeat the procedure using 5 mL of dimethylformamide R in place of solution A and make any necessary corrections. Calculate the content of water as a percentage.
Acidity. Dissolve a quantity containing the equivalent of 1.0 g of anhydrous Benzoyl peroxide in 25 mL of acetone R, add 75 mL of water, and filter. Wash the residue with two quantities of 10 mL of water. Combine the filtrate and washings, and titrate with sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS, using 0.25 mL of phenolphthalein/ethanol TS as indicator, until the change in colour is observed. Repeat the procedure without the substance being examined. The difference between the titrations represents the amount of sodium hydroxide required; not more than 1.25 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R4 as the coating substance and a mixture of 40 volumes of light petroleum R1, 20 volumes of toluene R, 15 volumes of acetone R, and 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of 4 freshly prepared solutions in acetone R containing (A) a quantity equivalent to 40 mg of anhydrous Benzoyl peroxide per mL, (B) 0.4 mg of anhydrous Benzoyl peroxide per mL, (C) 0.6 mg of benzoic acid R per mL, and for solution (D) mix 0.4 mL of benzyl benzoate R with 5 mL of acetone R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent. To 1.0 mL of this solution add 1.0 mL of solution A and dilute to 10ml with acetone R. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air for 20 minutes, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
Any spot corresponding to benzoic acid obtained with solution A is not more intense than that obtained with solution C (1.5%). Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot and the spot corresponding to benzoic acid, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B (1%). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution D shows two clearly separated principal spots.
Assay. Immediately before testing dissolve 2.5 g in sufficient dimethylformamide R to produce 100ml (solution A). To 5.0 mL of solution A add 20ml of acetone R and 5ml of potassium iodide (300 g/l) TS. Mix, allow to stand for 1 minute, and titrate with sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/l) VS until the solution is colourless. Repeat the procedure using 5 mL of dimethylformamide R in place of solution A and make any necessary corrections.
Each mL of sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 12.11mg of C14H10O4.