Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Hydroxocobalamin (Hydroxocobalaminum)
Hydroxocobalamin anhydrous
Hydroxocobalamin hydrate
Molecular formula. C62H89CoN13O15P (anhydrous); C62H89CoN13O15P,H2O (monohydrate).
Relative molecular mass. 1346 (anhydrous); 1365 (monohydrate).
Graphic formula.
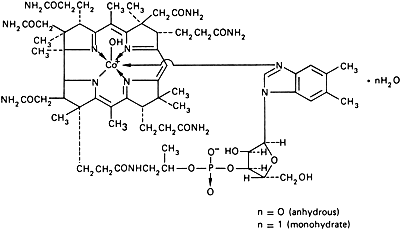
Chemical name. Cobinamide dihydroxide dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-α-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole; cobinamide dihydrogen phosphate (ester)-mono(inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-α-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole; Coα-[α-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)]-Coβ-hydroxocobamide; CAS Reg. No. 13422-51-0 (anhydrous). Cobinamide dihydroxide monohydrate, dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt), 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-α-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole; cobinamide dihydroxide monohydrate, dihydrogen phosphate (ester), mono(inner salt) 3'-ester with 5,6-dimethyl-1-α-D-ribofuranosyl-1H-benzimidazole; Coα-[α-(5,6-dimethylbenzimidazolyl)]-Coβ-hydroxocobamide monohydrate; CAS Reg. No. 13422-52-1 (monohydrate).
Other names. Vitamin B12a for anhydrous Hydroxocobalamin and Vitamin B12b for Hydroxocobalamin hydrate.
Description. Dark red crystals or a red, crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Sparingly soluble in water and ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in acetone R
Category. Antianaemia drug.
Storage. Hydroxocobalamin should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light and stored at a temperature between 2° and 8°C.
Labelling. The designation on the container should state whether the substance is in the anhydrous or hydrated form.
Additional information. In aqueous solution, Hydroxocobalamin exists as hydroxocobamide in equilibrium with the hydrated ionic form. The anhydrous form of Hydroxocobalamin is very hygroscopic. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Hydroxocobalamin contains not less than 96.0% and not more than 102.0% of C62H89CoN13O15P, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
A. The absorption spectrum of a 40 μg/mL solution in pH 4.5 acetate buffer TS, when observed between 230 nm and 550 nm, exhibits 3 maxima at about 274 nm, 351 nm, and 525 nm; the ratio of the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at 525 nm to that at 351 nm is about 0.34, and the ratio of the absorbance at 274 nm to that at 351 nm is about 0.80.
B. Heat cautiously about 2 mg in a porcelain crucible with a few drops of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS until a faintly bluish residue is produced. Cool, add 0.05 mL of water and then a few drops of a saturated solution of ammonium thiocyanate R; a blue-green colour is produced.
C. Place about 2 mg in a 100-mL glass-stoppered flask, dissolve in 2 mL of water and add 5 mL of phosphoric acid (~1440 g/l) TS. Insert in the flask a flat-bottomed glass tube 1 cm in diameter and 2 cm long, containing 1 mL of lithium carbonate/trinitrophenol TS. Close the flask and expose it for 4 hours to a bright light; the colour of the reagent in the glass tube remains unchanged (distinction from cyanocobalamin).
Loss on drying. Dry Hydroxocobalamin hydrate at 100°C under reduced pressure (not exceeding 0.6 kPa or about 5 mm of mercury) for 2 hours; it loses between 140 mg/g and 180 mg/g.
pH value. pH of a 20 mg/mL solution in carbon-dioxide-free water R, 8.0-10.0.
Other cobalamins. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.3 Column chromatography, shaking 20 g of diethylaminoethylcellulose R with 200 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.5 mol/l) VS, dilute with water to obtain a homogeneous suspension, allow to settle, and discard the supernatant liquid. Using a suitable filter, wash with water until the washings are free from alkali, then transfer the adsorbent to a tube, length 22 cm, diameter 1.2 cm, and provided with a stopcock. Allow to settle and tap the tube until the height of the adsorbent is about 14 cm. Wash with water until the pH of the eluate is the same as that of the water.
Similarly prepare a second column, slurrying carboxymethylcellulose R with hydrochloric acid (0.5 mol/l) VS, dilute with water, allow to settle, and discard the supernatant liquid. Using a suitable filter, wash with water until the washings are free from acid, then transfer the adsorbent to a tube, length 22 cm, diameter 1.2 cm, and provided with a stopcock. Allow to settle and tap the tube until the pH of the eluate is the same as that of the water.
Cover each column with a plug of glass wool and allow to drain until only a small amount of water remains above the adsorbents.
Place the column of diethylaminoethylcellulose above the other column so that the effluent runs into the carboxymethylcellulose.
Weigh accurately about 0.05 g of the substance to be examined, dissolve it in 20 mL of water, and acidify with sufficient hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS to obtain a pH of 4.0. Introduce this solution to the diethylaminoethylcellulose column and allow it to run through both columns, rejecting the first colourless eluate. Elute with water, the pH of which has previously been adjusted to 4.0 with hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS. Collect the coloured eluate into a 50-mL volumetric flask and adjust to volume with water. Measure the absorbance of this solution in a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 361 nm and calculate the content of other cobalamins in mg/g, using the absorptivity value of 20.7 (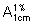 = 207); not more than 30 mg/g.
= 207); not more than 30 mg/g.
Acidic impurities. Elute the diethylaminoethylcellulose column from the above test for other cobalamins with sodium chloride (10 g/l) TS, collecting 50 mL of eluate. Measure the absorbance of this solution in a 1-cm layer at the maximum between 351 nm and 361 nm, and calculate the content of acidic impurities in mg/g, using the absorptivity value of 19.0 (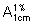 = 190); not more than 30 mg/g.
= 190); not more than 30 mg/g.
Assay
• The solutions must be protected from light throughout the assay.
Dissolve about 20 mg, accurately weighed, in sufficient acetate buffer, pH 4.5, TS to produce 500 mL. Measure the absorbance of this solution in a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 351 nm and calculate the content of C62H89CoN13O15P, using the absorptivity value of 19.5 (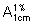 = 195).
= 195).
Additional requirements for Hydroxocobalamin for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 0.4 IU of endotoxin RS per mg.