Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Isoniazid (Isoniazidum)
Molecular formula. C6H7N3O
Relative molecular mass. 137.1
Graphic formula.
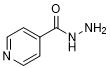
Chemical name. Pyridine-4-carbohydrazide; Isonicotinic acid hydrazide.
CAS Registry Number. 54-85-3.
Description. White or almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water R, sparingly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS; practically insoluble in heptane R.
Category. Tuberculostatic.
Storage. Isoniazid should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Isoniazid may exhibit polymorphism.
Requirements
Definition. Isoniazid contains not less than 99.0% and not more than 101.0% of C6H7N3O, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
-
Either test A alone or any two of tests B, C or D may be applied.
-
Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from isoniazid RS or with the reference spectrum of isoniazid ( The reference spectrum was recorded using isoniazid recrystallized from dehydrated ethanol.)
If the spectra thus obtained are not concordant, repeat the test using the residues obtained by separately dissolving the test substance and isoniazid RS in a small amount of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and evaporating to dryness. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from isoniazid RS.
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions given under "Related substances" with the following modification. For solution (1), use a solution containing 0.1 mg of the test substance per mL of mobile phase A. For solution (2), use a solution containing 0.1 mg of isoniazid RS per mL of mobile phase A. Inject 10 µL of solutions (1) and (2). The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
-
Carry out as described under 1.6 Spectrophotometry in the visible and ultraviolet regions. Use a 0.01 mg per mL solution of the test substance in methanol R. The absorption spectrum of the test solution, when observed between 200 nm and 400 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 263 nm.
Alternatively, and in combination with identity test B, where a diode-array detector is available, record the UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatograms with a diode array detector in the range of 200 nm to 400 nm. The UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the UV spectrum of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 5 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 2 volumes of acetone R, 2 volumes of methanol R, and 1 volume of water R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μL of each of the following solutions. For solution (A), dissolve 0.10 g of the test substance in 10 mL of methanol R. For solution (B), use a solution containing 10 mg of isoniazid RS per mL of methanol R. Develop the plate. After removing it from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (A) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity with the spot due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (B).
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 1; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution containing 0.50 g of the test substance in 10 mL of water R is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7, when compared as described under 1.11.2 Degree of coloration of liquids, Method II.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105 °C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
pH value (1.13). pH of a 0.05 g/mL solution of the test substance in carbon-dioxide-free water R, 6.0-8.0.
Impurity E (hydrazine). Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm). As the mobile phase, use a mixture of water R and acetonitrile R (40:60 V/V).
Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 300 nm.
Prepare as a diluent a mixture of 50 volumes of water R and 50 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Prepare the following solutions freshly:
For solution (A), dilute 1 mL of benzaldehyde R to 50 mL with methanol R. Use this solution within 4 hours.
For solution (1), transfer 50.0 mg of the test substance to a 10 mL volumetric flask. Dissolve the substance in 1 mL of water R, add 5 mL of solution (A), mix and allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent.
For solution (2), transfer 20.0 mg of hydrazine sulfate R (equivalent to 4.925 mg of hydrazine) to a 50 mL volumetric flask. Dissolve the substance in water R and dilute to volume with the same solvent. Dilute 2.5 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 25 mL volumetric flask, add 2.5 mL of solution (A), mix and allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent. Dilute 15.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with the diluent.
For solution (3), transfer 1 mL of water R to a 25 mL volumetric flask, add 2.5 mL of solution (A), mix and allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent. Dilute 15.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with the diluent.
Inject 10 µL each of solutions (1), (2) and (3) and record the chromatograms for about 30 minutes.
Use the chromatograms obtained with solutions (2) and (3) to identify the peak due to the reaction product of benzaldehyde and hydrazine, benzaldehyde azine (benzaldehyde azine is eluted at about 20 minutes). The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2), the signal-to-noise ratio of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine is at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to benzaldehyde azine in not greater than the area of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (15 ppm).
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated and end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
-
mobile phase A: a mixture of 0.5 volume of acetonitrile R and 100 volumes of ammonium formate buffer, pH 7.2;
-
mobile phase B: a mixture of 50 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of phosphate buffer pH 7.2.
Prepare the ammonium formate buffer by dissolving 0.315 g of ammonium formate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding ammonia (~10 g/L) TSand diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
Prepare the phosphate buffer pH 7.2 by dissolving 2.64 g of diammonium hydrogen phosphate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding phosphorous acid (~105 g/L) TS and diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Comments |
|
0–9 |
99.5 |
0.5 |
Isocratic |
|
9–22 |
99.5 to 85 |
0.5 to 15 |
Linear gradient |
|
22-35 |
85 to 60 |
15 to 40 |
Linear gradient |
|
35-36 |
60 |
40 |
Isocratic |
|
36–37 |
60 to 99.5 |
40 to 0.5 |
Return to initial composition |
|
37–45 |
99.5 |
0.5 |
Re-equilibration |
Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 266 nm.
Prepare the following solutions freshly using mobile phase A as a diluent.
For solution (1), dissolve 25.0 mg of the test substance and dilute to 25.0 mL. For solution (2), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 100.0 mL. For solution (4), dissolve 5 mg of isonicotinic acid R (impurity A), 5 mg of isonicotinamide R (impurity B), 5 mg of nicotinoyl hydrazide R (impurity D), 5 mg of benzoyl hydrazide (impurity G), and 5 mg of 3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine (impurity I) and dilute to 50.0 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with solution (1).
Inject 5 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (3) and (4).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) to identify the peaks due to the impurities A, B, D, G and I. The impurities are eluted, if present, at the following relative retention with reference to isoniazid (retention time about 11.7 minutes): impurity A about 0.32; impurity D about 1.15; impurity B about 1.30, impurity F about 1.59; impurity H about 1.98; impurity G about 2.05; impurity C about 2.11; impurity I about 2.38.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4), the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 2.0, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to isoniazid. Also, the test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak due to isoniazid is detected with a signal-to-noise ratio of at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.5, is not greater than 0.15 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.4, is not greater than 0.15 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity G, when multiplied with a correction factor of 2.6, is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity I, when multiplied with a correction factor of 0.33, is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %); and
-
the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than 0.1 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10 %).
-
The sum of the areas of all impurity peaks, including the corrected areas of any peaks corresponding to impurities A, B, G and I, is not greater than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5 %). Disregard any peaks with an area of less than the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.05%).
Assay. Dissolve 0.250 g of the test substance in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. To 20.0 mL of this solution, add 100 mL of water R, 20 mL of hydrochloric acid (~250 g/L) TS, 0.2 g of potassium bromide R, and 0.05 mL of methyl red/ethanol TS. Titrate with potassium bromate (0.0167 mol/L) VS, adding the titrant drop by drop and shaking till the red colour disappears. Each mL of potassium bromate (0.0167 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 3.429 mg of C6H7N3O.
Impurities
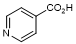
A. Pyridine-4-carboxylic acid (isonicotinic acid, isoniacin) (synthesis related impurity and degradation product);
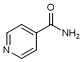
B. Pyridine-4-carboxamide (isonicotinamide) (synthesis related impurity);
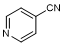
C. Pyridine-4-carbonitrile (4-cyanopyridin; isonicotinonitrile) (synthesis related impurity);
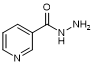
D. Pyridine-3-carbohydrazide (nicotinoyl hydrazide) (synthesis related impurity);
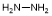
E. Hydrazine (synthesis related impurity and degradation product);
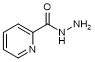
F. Pyridine-2-carbohydrazide (picolinohydrazide; 2-isoniazid) (synthesis related impurity);
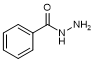
G. Benzohydrazide (Benzoyl hydrazine; benzhydrazide) synthesis related impurity);
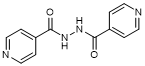
H. N'-(Pyridine-4-carbonyl)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide (1,2-Diisonicotinoylhydrazine; 1,2-Bis(4-pyridylcarbonyl)hydrazine; N '-Isonicotinoylisonicotinohydrazide) (synthesis related impurity);
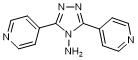
I. 3,5-Di(pyridin-4-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine (synthesis related impurity).