Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Ivermectin (Ivermectinum)
Molecular formula.
|
Component |
Molecular formula |
|
H2B1a |
C48H74O14 |
|
H2B1b |
C47H72O14 |
Relative molecular mass. Component H2B1a 875.1; Component H2B1b 861.1.
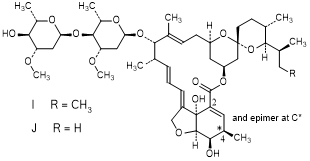
Graphic formula.
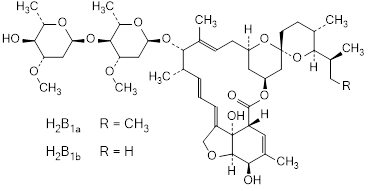
Chemical name. Mixture of (2aE,4E,5'S,6S,6'R,7S,8E,11R,13R,15S,17aR,20R,20aR, 20bS)-6'-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-7-{[2,6-dideoxy-4-O-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-α-l-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-3-O-methyl-α-l-arabino-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-20,20b-dihydroxy-5',6,8,19-tetramethyl-3',4',5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-tetradecahydrospiro[11,15-methano-2H,13H,17H-furo[4,3,2-pq][2,6]benzodioxacyclooctadecene-13,2'-[2H]pyran]-17-one (component H2B1a) and (2aE,4E,5'S,6S,6'R,7S,8E,11R,13R,15S,17aR,20R, 20aR,20bS)-7-{[2,6-dideoxy-4-O-(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-α-l-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-3-O-methyl-α-l-arabino-hexopyranosyl]oxy}-20,20b-dihydroxy-5',6,8,19-tetramethyl-6'-(propan-2-yl)-3',4',5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-tetradecahydrospiro[11,15-methano-2H,13H,17H-furo[4,3,2-pq][2,6]benzodioxacyclooctadecene-13,2'-[2H]pyran]-17-one (or 5-O-demethyl-25-de[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-25-(propan-2-yl)-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a) (component H2B1b) (IUPAC), Avermectin A1a, 5-O-demethyl-22,23-dihydro- (component H2B1a) and Avermectin A1a, 5-O-demethyl-25-de(1-methylpropyl)-22,23-dihydro-25-(1-methylethyl)- (component H2B1b) (CAS).
CAS Reg. N°70288-86-7, 71827-03-7 (component H2B1a), 70209-81-3 (component H2B1b)
Description. A white or yellowish-white, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in dichloromethane R, soluble in dehydrated ethanol R.
Category. Antiparasitic.
Storage. Ivermectin should be kept in tightly closed containers, protected from light. It should be stored between 2 °C and 8 °C. Where the use of an antioxidant is allowed, store at 25° C. Excursions are permitted between 15 °C and 30 °C.
Additional information. Ivermectin is slightly hygroscopic. It is a semisynthetic product derived from a fermentation product.
Requirements
Definition. Ivermectin contains not less than 95.0% and not more than 102.0% of the sum of the Ivermectin components H2B1a (C48H74O14) and H2B1b (C47H72O14), calculated with reference to the anhydrous and solvent-free substance. The ratio of the area percentages of component H2B1a / (H2B1a + H2B1b) is not less than 90.0%.
Identity tests.
- Either test A alone or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from ivermectin RS or with the reference spectrum of ivermectin.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the conditions given under “Assay”. The retention times of the principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) correspond to the retention times of the peaks due to ivermectin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography using silica gel R4 or R2 as the coating substance and a mixture of 90 volumes of dichloromethane R, 8 volumes of methanol R and 0.8 volume of ammonia (~260 g/L) TS as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 30 µL of each of the following two solutions in methanol R containing (A) 7 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 7 mg of ivermectin RS per mL. Develop the plate. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air or in a current of air. Examine the chromatogram under ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The two partly separated spots in the chromatogram obtained with solution (A) correspond in position, appearance and intensity with the two partly separated principal spots due to ivermectin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (B).
Specific optical rotation (1.4). Dissolve 0.250 g of the test substance in methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent; 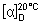 = −20 to –17 with reference to the anhydrous and solvent-free substance.
= −20 to –17 with reference to the anhydrous and solvent-free substance.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g, using about 1.0 g of the substance.
Clarity and colour of solution. Dissolve 1.0 g in 50 mL toluene R. This solution is clear and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7, when compared as described under 1.11.2 Degree of coloration of liquids, Method II.
Water. Determine, as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using 0.500 g of the substance; the water content is not more than 10 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.4 High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions given below under “Assay”.
Prepare the following solutions in methanol R. For solution (1), use solution (1) as described under “Assay”. For solution (2), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 100.0 mL.
Inject alternately 20 μL each of solution (1), (2) and (3). Record the chromatograms for about two times the retention time of the principal peak.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1), the resolution between the peak due to component H2B1b (with a relative retention time of about 0.74 with reference to component H2B1a) and the peak due to component H2B1a (retention time about 23 minutes) is at least 3.0. In the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the signal-to-noise ratio of the peak due to ivermectin is at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the area of any impurity peak with a relative retention of 1.3 to 1.5 with reference to the peak due to H2B1a is not greater than 2.5 times the area of the peak due to H2B1a in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (2.5%);
- the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than the area of the peak due to H2B1a in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1 %).
- The sum of the areas of all impurity peaks is not greater than five times the area of the peak due to H2B1a in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (5%). Disregard any peak with an area less than the area of the peak due to H2B1a in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.05%).
Ethanol and formamide. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Gas chromatography, using a fused-silica capillary column 30 m long and 0.53 mm in internal diameter coated with macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness: 1 µm).
As a detector, use a flame ionization detector. Keep the detector at 250 °C. Use nitrogen for chromatography R as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 7.5 mL per minute. Use as split injection ratio of 1:10. Keep the injection port at 200 °C.
Use the gradient conditions described below.
|
Time |
Temperature |
Comment |
|
0–2 |
50° to 80° |
Linear gradient |
|
2–8 |
80° to 240° |
Linear gradient |
Prepare the following solutions:
Internal standard solution: dilute 0.5 mL of propanol R to 100.0 mL with water R.
For solution (1), transfer 120 mg of the test substance to a centrifuge tube, dissolve in 2.0 mL of m-xylene R (if the solution is hazy, heat slightly to 30–40 °C while mixing), add 2.0 mL of water R, mix thoroughly and centrifuge. Keeping the aqueous layer, remove the upper m-xylene layer and extract it with an additional 2.0 mL of water. Discard the m-xylene layer and combine the two aqueous layers. Add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Centrifuge and discard any remaining m-xylene.
For solution (2), dilute 3.0 g of dehydrated ethanol R to 100.0 mL with water R.
For solution (3), dilute 1.0 g of formamide R to 100.0 mL with water R.
For solution (4), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) and 5.0 mL of solution (3) to 50.0 mL with water R. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a centrifuge tube, add 2.0 mL of m-xylene R, mix thoroughly and centrifuge. Remove the upper layer and extract it with 2.0 mL of water R. Discard the upper layer and combine the aqueous layers. Add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Centrifuge and discard any remaining m-xylene.
For solution (5), dilute 10.0 mL of solution (2) and 10.0 mL of solution (3) to 50.0 mL with water R. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a centrifuge tube, add 2.0 mL of m-xylene R, mix thoroughly and centrifuge. Remove the upper layer and extract it with 2.0 mL of water R. Discard the upper layer and combine the aqueous layers. Add 1.0 mL of the internal standard solution. Centrifuge and discard any remaining m-xylene.
Inject alternately 1 µL each of solutions (1), (4) and (5). Prepare calibration plots for ethanol and formamide by plotting the ratios of peak responses of any peak due to ethanol or formamide to the area of the corresponding peak due to the internal standard versus the concentrations of solutions (4) and (5). Determine the concentration of ethanol and formamide in solution (1), if present. In the event the peak response is significantly outside the range found with solutions (4) and (5), additional dilutions of solutions (2) and (3) should be prepared and injected to obtain peak responses framing those found for solution (1); not more than 50 mg/g of ethanol and not more than 30 mg/g of formamide.
Assay. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless-steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm).
As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 15 volumes of water R, 34 volumes of methanol R and 51 volumes of acetonitrile R. Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 254 nm.
Prepare the following solutions in methanol R. For solution (1), dissolve 40.0 mg of the test substance and dilute to 50.0 mL. For solution (2), dissolve 40.0 mg of ivermectin RS and dilute to 50.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 100.0 mL.
Inject alternately 10 μL each of solution (1), (2) and (3). Record the chromatograms for about two times the retention time of the principal peak.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2), the resolution between the peaks due to component H2B1b (with a relative retention of about 0.74 with reference to component H2B1a) and due to component H2B1a (retention time about 23 minutes) is at least 3.0.
Measure the areas of the peaks corresponding to the components H2B1a and H2B1b obtained in the chromatograms of solutions (1), (2) and (3) and calculate the percentage content of ivermectin component H2B1a by comparing the peak areas due the component H2B1a in the chromatograms obtained with solutions (1) and (2) and the percentage content of ivermectin component H2B1b by comparing the peak area due the component H2B1b in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) with the peak area due the component H2B1a in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), considering the assigned content of component H2B1a in ivermectin RS.
Impurities.
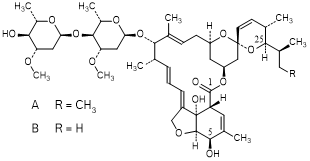
A. 5-O-demethylavermectin A1a (avermectin B1a) (synthesis-related impurity).
B. 5-O-demethyl-25-de(butan-2-yl)-25-(propan-2-yl)avermectin A1a (avermectin B1b) (synthesis-related impurity).
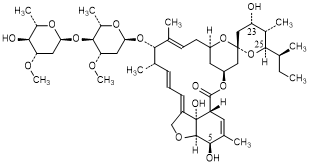
C. (23S)-5-O-demethyl-23-hydroxy-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a (avermectin B2a) (synthesis-related impurity).
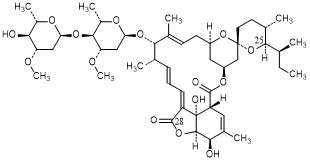
D. 5-O-demethyl-28-oxo-22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a (28-oxoH2B1a) (degradation product).
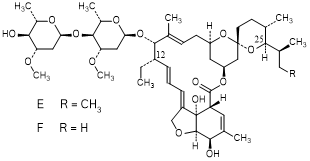
E. 5-O,12-didemethyl-12-ethyl-22,23-dihydroavermectinA1a (12-demethyl-12- ethylH2B1a) (degradation product).
F. 25-de(butan-2-yl)-5-O,12-didemethyl-12-ethyl-25-(propan-2-yl)-22,23-di-hydroavermectin A1a (12-demethyl-12-ethylH2B1b) (degradation product).
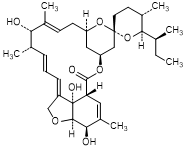
G. (2aE,4E,5'S,6S,6'R,7S,8E,11R,13R,15S,17aR,20R,20aR,20bS)-6'-[(2S)-butan-2-yl]-7,20,20b-dihydroxy-5',6,8,19-tetramethyl-3',4',5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-tetradecahydrospiro[11,15-methano-2H,13H,17H-furo[4,3,2-pq][2,6]benzodioxacyclooctadecene-13,2'-[2H]pyran]-17-one (H2B1a aglycone) (degradation product).
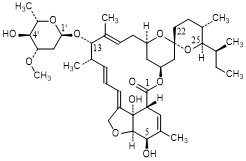
H. -4'-O-de(2,6-dideoxy-3-O-methyl-α-l-arabino-hexopyranosyl)-5-O-demethyl -22,23-dihydroavermectin A1a (degradation product).
I. 2,3-didehydro-5-O-demethyl-3,4,22,23-tetrahydroavermectin A1a (Δ2,3H2B1a) (degradation product).
J. 25-de(butan-2-yl)-2,3-didehydro-5-O-demethyl-25-(propan-2-yl)-3,4,22,23-tetrahydroavermectin A1a (Δ2,3H2B1b) (degradation product).
K. (4RS)-5-O-demethyl-3,4,22,23-tetrahydroavermectin A1a (H4B1a isomers) (synthesis-related impurity).