Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Lactose (Lactosum)
Lactose, anhydrous
Lactose monohydrate
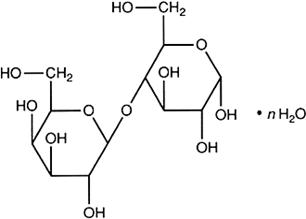
n = 0 (anhydrous)
n = 1 (monohydrate)
C12H22O11 (anhydrous)
C12H22O11,H2O (monohydrate)
Relative molecular mass. 342.3 (anhydrous); 360.3 (monohydrate).
Chemical name. Lactose; 4-O-ß-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucose; CAS Reg. No. 63-42-3.
Lactose monohydrate; 4-O-ß-D-galactopyranosyl-D-glucose monohydrate; CAS Reg. No. 64044-51-5.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Freely but slowly soluble in water; very slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Tablet and capsule diluent.
Storage. Lactose should be kept in a well-closed container.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Lactose should state whether it is the monohydrate or the anhydrous form.
Additional information. Attention should be paid to the microbiological purity, since Lactose is of natural origin.
Requirements
Identity tests
A. Dissolve 0.1 g in 10 mL of water, add 3 mL of potassio-cupric tartrate TS, and heat; a red precipitate is formed.
B. Dissolve 0.25 g in 5 mL of water, add 5 mL of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, and heat in a water-bath at 80 °C for 10 minutes; a red colour develops.
C. Dissolve 20 mg in 5 mL of water, add 0.2 mL of methylamine hydrochloride (20 g/l) TS, and heat to boiling for 30 seconds. Add 0.2 mL of sodium hydroxide (~200 g/l) TS; the initial yellow colour of the solution turns to red.
Specific optical rotation. Dissolve 10 g in 80 mL of water while heating to 50 °C. Allow to cool and add 0.2 mL of ammonia (~100 g/l) TS. After 30 minutes dilute to 100 mL with water. Measure the rotation at 20 °C and calculate with reference to the anhydrous substance; 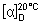 = +54.4° to +55.9°.
= +54.4° to +55.9°.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution, add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS and proceed as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 1; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 5 μg/g.
Starch. Dissolve 1.5 g in 10 mL of boiling water. Cool, and add 1 drop of iodine (0.05 mol/l) VS; no blue colour develops.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 3 g in 10 mL of boiling water is colourless or nearly colourless, clear, and odourless.
Ethanol-soluble substances. Add 10 g of finely powdered Lactose to 40 mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and shake for 10 minutes. Filter, evaporate 10 mL of the filtrate to dryness, dry the residue at 100 °C for 10 minutes, and weigh; not more than 20 mg.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using either:
- 2 g of anhydrous Lactose; the water content is not more than 10 mg/g; or
- 0.5 g of Lactose monohydrate; the water content is not less than 45 mg/g and not more than 55 mg/g.
Acidity or alkalinity. Boil 6 g with 25 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R, cool, and add 0.3 mL of phenolphthalein/ethanol TS; the solution remains colourless. Titrate with carbonate-free sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS; not more than 0.4 mL is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (pink).