Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Levonorgestrel (Levonorgestrelum)
Molecular formula. C21H28O2
Relative molecular mass. 312.5
Graphic formula
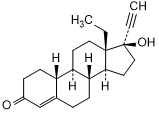
Chemical name. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one; CAS Reg. No. 797-63-7.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water R; sparingly soluble in dichloromethane R, slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Category. Contraceptive.
Storage. Levonorgestrel should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Requirements
Definition. Levonorgestrel contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C21H28O2, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
- Either tests A and C or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from levonorgestrel RS or with the reference spectrum of levonorgestrel.
B. Carry out the examination as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the conditions described under "Related substances", method A. Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) dissolve 10 mg of the test substance in 7 mL of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 10 mL with water R. Dilute 1 volume to 100 volumes with a solvent mixture consisting of 30 volumes of water R and 70 volumes of acetonitrile R. For solution (2) use a solution containing 0.01 mg levonorgestrel RS per mL of the same solvent mixture. Inject 50 µL of solution (1) and (2). The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained from solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to levonorgestrel in the chromatogram obtained from solution (2).
C. Determine the specific optical rotation (1.4) using a 10 mg per mL solution of the test substance in dichloromethane R. Calculate with reference to the dried substance; the specific optical rotation is between -35° to -30°.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 3.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105 °C; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Related substances
- Perform test A and B.
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octylsilyl gel groups (5 µm). The material contains embedded polar groups.
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
Mobile phase A: Mix 400 volumes of acetonitrile R with 600 volumes of water R.
Mobile phase B: Use acetonitrile R.
Time (min)
Mobile phase A
(%v/v)Mobile phase B
(%v/v)Comments
0–50
100 to 20
0 to 80
Linear gradient
50–51
20 to 100
80 to 0
Return to initial composition
51–65
100
0
Re-equilibration
Operate with a flow of 0.7 mL/min. As a detector use a n ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 215 nm and, for impurity O, at 200 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 30 °C.
Prepare as a solvent solution a mixture of 30 volumes of water R and 70 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) dissolve 10.0 mg of the test substance in 7 mL of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. For solution (2) dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 1000 volumes with the solvent solution. For solution (3) dissolve 5 mg of levonorgestrel for system suitability 1 RS (containing the impurities A, H, K, M, O and S) in 3.5 ml of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 5.0 mL with water R. For solution (4) dissolve 5.0 mg of levonorgestrel impurity B RS in 35 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent solution. For solution (5) dissolve 5.0 mg of norethisterone RS (impurity U) in 35 mL of acetonitrile R and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with solution (2).
Inject 50 µL of solution (3). The test is not valid unless the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 3.0, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity M and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to impurity A.
Inject alternately 50 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (4) and (5).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) and the chromatogram supplied with levonorgestrel for system suitability 1 RS to identify the peaks due to the impurities A, H, K, M and S, and at 200 nm to identify the peak due to impurity O. Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) to identify the peak due to impurity B and the chromatogram obtained with solution (5) to identify the peak due to impurity U.
The impurities are eluted at the following relative retentions with reference to levonorgesterel (retention time about 20 minutes): impurity H about 0.5; impurity U about 0.8; impurity K about 0.85; impurity A about 0.91; impurity M about 0.95; impurity O about 1.16; impurity B about 1.26; and impurity S about 1.9.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A, when multiplied by a correction factor of 0.4, is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.3%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (4) (0.3%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity K is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.3%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity M, when multiplied by a correction factor of 3.1, is not greater than 2 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.2%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity O, recorded at 200 nm, when multiplied by a correction factor of 2.6, is not greater than 3 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.3%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity S is not greater than 2 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.2%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity U, is not greater than 2 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (5) (0.2%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity H is not greater than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.15%);
- the area of any other peak, other than the principal peak due to levonorgestrel, is not greater than the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.10%).
- determine the sum of the corrected areas of any peak corresponding to impurity A and M and the areas of all other peaks, other than the principal peak or any peak corresponding to impurity O, B or U, using solution (2) as a reference solution. Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (0.05%). Calculate the sum of all impurities considering the concentrations found for impurity B and U. The sum of all impurities is not greater than 1.0 %.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl gel groups (3 µm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
mobile phase A: Mix 400 volumes of acetonitrile R with 600 volumes of water R;
mobile phase B: Mix 100 volumes of water R with 900 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Time (min)
Mobile phase A
(%v/v)Mobile phase B
(%v/v)Comments
0–1
92
8
Isocratic
1–3
92 to 82
8 to 18
Linear gradient
3–6
82
18
Isocratic
6–16
82 to 60
18 to 40
Linear gradient
16–21
60 to 0
40 to 100
Linear gradient
21–32
0
100
Isocratic
32–33
0 to 92
100 to 8
Return to initial composition
33–50
92
8
Re-equilibration
Operate with a flow of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 200 nm.
Prepare as a solvent solution a mixture of 30 volumes of water R and 70 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) dissolve 10.0 mg of the test substance in 7 mL of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 10.0 mL with water R. For solution (2) dissolve 5 mg of levonorgestrel for system suitability 2 RS (containing the impurities V and W) in 3.5 mL of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 5.0 mL with water R. For solution (3) dissolve 5.0 mg of ethinylestradiol RS in 35 mL of acetonitrile R using sonication and dilute to 50.0 mL with water R. Dilute 3.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Inject 50 µL of solution (2). The assay is not valid unless the resolution factor between the two principal peaks due to levonorgestrel (retention time about 12 minutes) and the peak due to impurity W (with a relative retention of about 0.9) is at least 1.5.
Inject alternately 50 µL each of solutions (1) and (3).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) and the chromatogram supplied with levonorgestrel for system suitability 2 RS to identify the peaks due to the impurities V and W. The impurities are eluted at the following relative retentions with reference to levonorgesterel (retention time about 12 minutes): impurity W about 0.9 and impurity V about 1.9.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity W is not greater than the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (3) (0.3%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity V is not greater than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (3) (0.15%).
Assay. Dissolve 0.20 g, accurately weighed, in 45 mL of tetrahydrofuran R. Add 10 mL of silver nitrate (100 g/L) TS. After 1 minute titrate with sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS, determining the end-point potentiometrically. Carry out a blank titration. 1 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS, is equivalent to 31.25 mg of C21H28O2.
Impurities
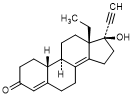
A. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4,8(14)-dien-20-yn-3-one
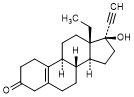
B. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
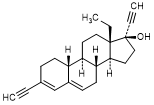
C. 13-ethyl-3-ethynyl-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-3,5-dien-20-yn-17-ol
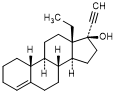
D. 13-ethyl-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-17-ol (3-deoxolevonorgestrel)
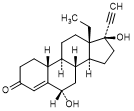
G. 13-ethyl-6α,17-dihydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one (6α-hydroxylevonorgestrel)
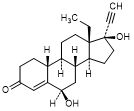
H. 13-ethyl-6β,17-dihydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one (6β-hydroxylevonorgestrel),
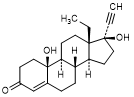
I. 13-ethyl-10,17-dihydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one (10-hydroxylevonorgestrel)
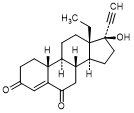
J. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yne-3,6-dione (6-oxolevonorgestrel)
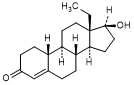
K. 13-ethyl-17β-hydroxygon-4-en-3-one (18-methylnandrolone)
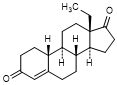
L. 13-ethylgon-4-en-3,17-dione (levodione)
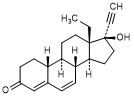
M. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-4,6-dien-20-yn-3-one (Δ6-levonorgestrel)
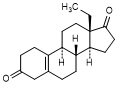
N. 13-ethylgon-5(10)-ene-3,17-dione
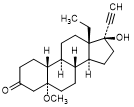
O. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-5-methoxy-18,19-dinor-5α,17α-pregn-20-yn-3-one (4,5-dihydro-5α-methoxylevonorgestrel)
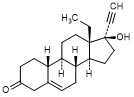
P. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-5-en-20-yn-3-one
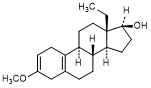
Q. 13-ethyl-3-methoxygona-2,5(10)-dien-17β-ol
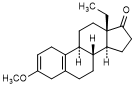
R. 13-ethyl-3-methoxygona-2,5(10)-dien-17-one
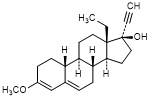
S. 13-ethyl-3-methoxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-3,5-dien-20-yn-17-ol
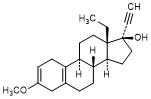
T. 13-ethyl-3-methoxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-2,5(10)-dien-20-yn-17-ol
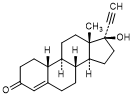
U. 17-hydroxy-19-nor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one (norethisterone)
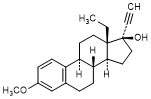
V. 13-ethyl-3-methoxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yn-17-ol
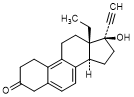
W. 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-5,7,9-trien-20-yn-3-one