Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Lumefantrine (Lumefantrinum)
C30H32Cl3NO
Relative molecular mass. 528.9
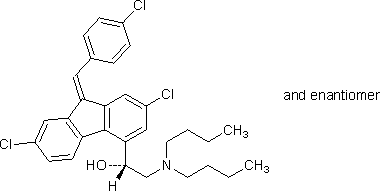
Chemical name. (1RS)-2-(dibutylamino)-1-{(9Z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]-9H-fluoren-4-yl}ethanol; CAS Reg. No. 82186-77-4
Other name. Benflumetol.
Description. A yellow crystalline powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; soluble in dichloromethane R; slightly soluble in methanol R .
Category. Antimalarial.
Storage. Lumefantrine should be kept in a well-closed container.
Additional information. Lumefantrine melts at 128–132°C.
Requirements
Definition. Lumefantrine contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.0% of C30H32Cl3NO, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity test
• Either tests A and B or test C may be applied.
A. Carry out test A.1 or, where UV detection is not available, test A.2.
A.1 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 40 volumes of light petroleum R1, 6 volumes of ethyl acetate R and 10 volumes of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 µl of each of 2 solutions in ethyl acetate R, containing (A) 10 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 10 mg of lumefantrine RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry exhaustively in air or in a current of cool air. Examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity to that obtained with solution B.
A.2 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using the conditions described above under test A.1 but using silica gel R5 as the coating substance. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry exhaustively in air or in a current of cool air and expose to iodine vapour until spots appear. Examine the chromatogram immediately in daylight.
The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity to that obtained with solution B.
B. Dissolve about 20 mg, accurately weighed, in 200 mL of methanol R by sonication for about 15 minutes. Allow the solution to cool to room temperature and dilute fivefold with methanol R. The absorption spectrum (1.6) of the diluted solution when observed between 275 and 325 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 302 nm; the specific absorbance (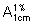 ) is between 314 and 348.
) is between 314 and 348.
C. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from lumefantrine RS or with the reference spectrum of lumefantrine.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3 and determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 10 μg/g.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on Drying. Dry for 3 hours at 105°C; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Related substances
• Either test A or test B may be applied
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (12.5 cm x 4.0 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 μm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
Mobile phase A: 200 volumes of ion pair reagent, 500 volumes of water R, 250 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of 1-propanol R.
Mobile phase B: 200 volumes of ion pair reagent, 100 volumes of water R, 650 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of 1-propanol R.
Mobile phase C: 100 volumes of water R, 100 volumes of acetonitrile R and 400 volumes of 1-propanol R.
Prepare the ion pair reagent by dissolving 5.65 g of sodium hexanesulfonate R and 2.75 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R in about 900 mL of water R. Adjust the pH to 2.3 using phosphoric acid (~105 g/l) TS, dilute to 1000 mL and filter through a 0.5 µm filter.
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Mobile phase C |
Comments |
|
0-14 |
25 |
75 |
0 |
Isocratic |
|
14-19 |
25 to 0 |
75 to 100 |
0 |
Linear gradient |
|
19-20 |
0 |
100 to 80 |
0 to 20 |
Linear gradient |
|
20-26 |
0 |
80 |
20 |
Isocratic |
|
26-27 |
0 |
80 to 30 |
20 to 70 |
Linear gradient |
|
27-50 |
0 |
30 |
70 |
Isocratic |
|
50-51 |
0 to 25 |
30 to 75 |
70 to 0 |
Return to initial composition |
|
51-56 |
25 |
75 |
|
Re-equilibration |
Prepare the following solutions in acetonitrile R. For solution (1) use 0.3 mg of the test substance per mL. For solution (2) dilute a suitable volume of solution (1) to obtain a concentration equivalent to 0.3 μg of lumefantrine per mL. For solution (3) dissolve 3 mg of lumefantrine for system suitability RS (containing lumefantrine and impurities A, B and C) in 10 mL.
Operate with a flow rate of 2.0 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 265 nm.
Inject 20 μl of solution (3). The impurity peaks are eluted at the following relative retention with reference to lumefantrine (retention time about 10 minutes): impurity A about 0.9; impurity B about 4.3 and impurity C about 4.6. The test is not valid unless the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 2.0, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from that due to lumefantrine. If necessary adjust the amount of acetonitrile in mobile phase A, or adjust the gradient programme.
Inject alternatively 20 μl each of solutions (1) and (2).
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) the area of any individual peak corresponding to either impurity B or impurity C is not greater than three times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.3%). The area of any other impurity peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.1%). The sum of the areas of all peaks, other than the principal peak, is not greater than five times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5 %). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%) and any peak resulting from the solvent.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 40 volumes of light petroleum R1, 6 volumes of ethyl acetate R and 10 volumes of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 µl of solutions (1), (3) and (4). Solution (1) contains 10 mg of the test substance per mL of ethyl acetate R. For solution (2) dilute 1 mL of solution (1) to 100 mL with ethyl acetate R. For solution (3) dilute 3 mL of solution (2) to 10 mL with ethyl acetate R. For solution (4) dilute 2 mL of solution (2) to 20 mL with ethyl acetate R. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry exhaustively in air or in a current of cool air. Examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) any spot, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.3%) and not more than two such spots are more intense than that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.1%).
Assay
Dissolve about 0.45 g, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid R1 by stirring for about 15 minutes, and titrate with perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS, determine the end-point potentiometrically as described under 2.6 Non aqueous titration, Method A. Each mL of perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 52.89 mg of C30H32Cl3NO.
Impurities
A. (2RS)-2-(dibutylamino)-2-{(9Z)-2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]-9H-fluoren-4-yl}ethanol,
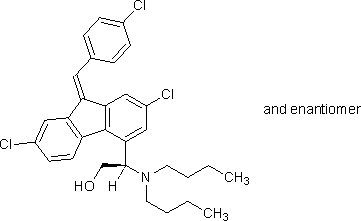
B. 1,4-bis{2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]-9H-fluoren-4-yl}-3,6-dioxabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane,
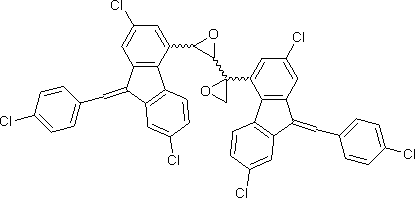
C. 2,3'-bis{2,7-dichloro-9-[(4-chlorophenyl)methylidene]-9H-fluoren-4-yl}-2,2'-bioxiranyl.