Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Magnesium stearate (Magnesii stearas)
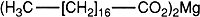
C36H70MgO4
Chemical name. Magnesium stearate; magnesium octadecanoate; CAS Reg. No. 557-04-0.
Description. A white, very fine powder of low bulk density; unctuous and readily adheres to the skin; odour, very faint, of stearic acid.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water, ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, and ether R; slightly soluble in hot ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Tablet and capsule lubricant; glidant; antiadherent.
Storage. Magnesium stearate should be kept in a well-closed container.
Requirements
Definition. Magnesium stearate consists mainly of magnesium stearate (C17H35CO2)2Mg with variable proportions of magnesium palmitate (C15H31CO2)2Mg and magnesium oleate (C17H33CO2)2Mg.
Magnesium stearate contains not less than 3.8% and not more than the equivalent of 5.8% of Mg, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
A. To 5 g add 50 mL of ether R, 20 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/l) TS, and 20 mL of water. Heat under a reflux condenser until completely dissolved, and allow to cool. Separate the aqueous layer, shake the ether layer with two quantities, each of 4 mL, of water, combine the aqueous solutions, wash with 15 mL of ether R, and dilute to 50 mL with water. (Retain this solution for identity test B and for "Chlorides".) Evaporate the ether layer to dryness and dry the residue at 105 °C. The congealing point of the residue is not lower than 53 °C. (Keep the residue for "Acid value of fatty acids".)
B. To 1 mL of the above aqueous solution, add 1 mL of ammonia (~100 g/l) TS; a white precipitate is formed which dissolves on the addition of 1 mL of ammonium chloride (100 g/l) TS. Add 1 mL of disodium hydrogen phosphate (40 g/l) TS; a white, crystalline precipitate is produced.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 4; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Chlorides. Proceed with 2 mL of the aqueous solution from identity test A as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 0.25 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant mass at 105 °C; it loses not more than 60 mg/g.
Acidity or alkalinity. Boil 1 g with 20 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R for 1 minute under constant shaking, cool, and filter. To 10 mL of the filtrate add 2 drops of bromothymol blue/ethanol TS and titrate with either hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS or sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS; not more than 0.05 mL of either titrant is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (green).
Acid value of fatty acids. Use 0.2 g of the residue obtained in identity test A and dissolve in 25 mL of the prescribed mixture of solvents; 195-210.
Assay. With caution, heat gently about 0.5 g, previously dried and accurately weighed, and gradually ignite until a white residue is obtained. Cool, add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS, and warm on a water-bath for 10 minutes. Dilute with 25 mL of hot water, add sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS until the solution becomes slightly turbid, and then add 10 mL of ammonium chloride buffer, pH 10.0, TS. Proceed with the titration as described under 2.5 Complexometric titrations for magnesium.
Each mL of disodium edetate (0.05 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 1.215 mg of Mg.