Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Mebendazole (Mebendazolum)
Molecular formula. C16H13N3O3
Relative molecular mass. 295.3
Graphic formula
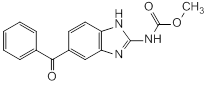
Chemical name. Methyl 5-benzoylbenzimidazole-2-carbamate, methyl (5-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate; CAS Reg. No. 31431-39-7.
Description. A white or almost white powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water, dilute mineral acids , dichloromethane and ethanol (~750 g/L) TS; freely soluble in formic acid (~1080 g/L) TS.
Category. Anthelmintic.
Storage. Mebendazole should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Mebendazole exhibits polymorphism.
Requirements
Definition. Mebendazole is polymorph C, the crystal form of mebendazole RS. Mebendazole contains not less than 99.0% and not more than 101.0% of mebendazole (C16H13N3O3), calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity test
Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum obtained from the solid state is concordant with the spectrum obtained from mebendazole RS (confirmation of polymorphic form C).
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry at 105 °C under reduced pressure (not exceeding 0.6 kPa or about 5 mm of mercury) for 4 hours; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (10 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (3 μm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
mobile phase A: 7.5 g/L solution of ammonium acetate R;
mobile phase B: Acetonitrile R.
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Comments |
|
0–15 |
80 to 70 |
20 to 30 |
Linear gradient |
|
15–20 |
70 to 10 |
30 to 90 |
Linear gradient |
|
20–25 |
10 |
90 |
Isocratic |
|
25–26 |
10 to 80 |
90 to 20 |
Return to initial composition |
|
26–36 |
80 |
20 |
Isocratic re-equilibration |
Operate with a flow rate of 1.2 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 250 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 40 °C.
Prepare the following solutions in dimethylformamide R. For solution (1) dissolve 25.0 mg of the test substance and dilute to 25.0 mL. For solution (2) dissolve 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL. For solution (3) dissolve 5.0 mg of mebendazole for system suitability RS (containing the impurities A, B, C, D, E, F and G) and dilute to 5.0 mL.
Inject 10 μL of solution (3). The test is not valid unless the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 4, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D (relative retention about 1.1) and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to mebendazole (retention time about 12 minutes).
Inject alternately 10 μL each of solution (1) and (2).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) and the chromatogram supplied with mebendazole for system suitability RS to identify the peaks due to the impurities A, B, C, D, E, F and G. The impurities are eluted at the following relative retention with reference to mebendazole (retention time about 12 minutes): impurity A about 0.4; impurity B about 0.5; impurity C about 0.7; impurity D about 1.1; impurity E about 1.3; impurity F about 1.4; and impurity G about 1.6.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A, impurity B, impurity C, impurity D, impurity E or impurity F is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.25%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity G, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.4, is not greater than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%);
- the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10%);
- the sum of the areas of all impurities is not greater than 4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.250 g, accurately weighed, in 3 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and add 50 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of anhydrous acetic acid R and 7 volumes of methyl ethyl ketone R. Titrate with perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS, determining the end-point potentiometrically as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration.
Each mL of perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 29.53 mg of C16H13N3O3.
Impurities
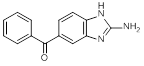
A. (2-Amino-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)phenylmethanone (degradation product)
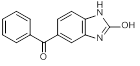
B. (2-Hydroxy-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)phenylmethanone
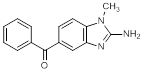
C. (2-Amino-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl)phenylmethanone
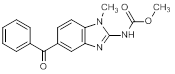
D. Methyl (5-benzoyl-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate
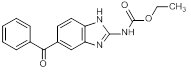
E. Ethyl (5-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate (synthesis-related impurity)
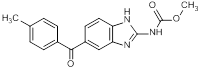
F. Methyl [5-(4-methylbenzoyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate (synthesis-related impurity)
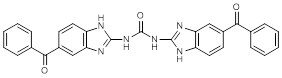
G. N,N'-bis(5-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)urea (synthesis-related impurity)