Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Mercaptopurine (Mercaptopurinum)
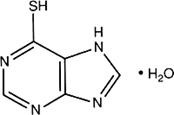
C5H4N4S,H2O
Relative molecular mass. 170.2
Chemical name. Purine-6-thiol monohydrate; 1,7-dihydro-6H-purine-6-thione monohydrate; CAS Reg. No. 6112-76-1.
Description. A yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water and ether R; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; dissolves in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
Category. Cytotoxic drug.
Storage. Mercaptopurine should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. CAUTION: Mercaptopurine must be handled with care, avoiding contact with the skin and inhalation of airborne particles.
It melts at a temperature exceeding 308 °C with decomposition.
Requirements
Mercaptopurine contains not less than 97.0% and not more than the equivalent of 102.0% of C5H4N4S, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
A. Dissolve 20 mg in 5 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide R and dilute to 100 mL with hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 200 mL with hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS. The absorption spectrum of the diluted solution, when observed between 230 nm and 350 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 325 nm.
B. Dissolve 20 mg in 20 mL of warm ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and add 1 mL of a saturated solution of mercuric acetate R in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; a white precipitate is produced.
C. Dissolve 20 mg in 20 mL of warm ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and add 1 mL of a solution containing 10 mg of lead acetate R per mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; a yellow precipitate is produced.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using 0.15 g; the water content is not less than 100 mg/g and not more than 120 mg/g.
Hypoxanthine. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R4 as the coating substance and a mixture of 90 volumes of acetone R, 7 volumes of water, and 3 volumes of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of two solutions containing (A) 50 mg of Mercaptopurine dissolved in 1 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide R and diluted to 10 mL with methanol R, and (B) 10 mg of hypoxanthine R dissolved in 10 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide R and diluted to 100 mL with methanol R. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.3 g, accurately weighed, in 80 mL of dimethylformamide R, add 5 drops of thymol blue/dimethylformamide TS, and titrate with sodium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS to a blue end-point, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method B.
Each mL of sodium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 15.22 mg of C5H4N4S.