Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Methyldopa (Methyldopum)
Molecular formula. C10H13NO4,11/2H2O
Relative molecular mass. 238.2
Graphic formula.
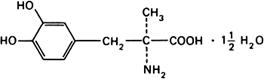
Chemical name. L-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine sesquihydrate; 3-hydroxy-α-methyl-L-tyrosine sesquihydrate; CAS Reg. No. 41372-08-1.
Description. White to yellowish white, fine powder or lumps; odourless.
Solubility. Slightly soluble in water and ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Antihypertensive.
Storage. Methyldopa should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Requirements
Definition. Methyldopa contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 101.0% of C10H13NO4, calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
• Either test A alone or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from methyldopa RS or with the reference spectrum of methyldopa.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using cellulose R2 as the coating substance and a mixture of 50 volumes of 1-butanol R, 25 volumes of glacial acetic acid R and 25 volumes of water as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of 2 solutions in hydrochloric acid (1 mol/l) VS containing (A) 10 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 10 mg of methyldopa RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in a current of warm air, spray with a freshly prepared solution composed of 2 volumes of ferric chloride (25 g/l) TS and 1 volume of potassium ferricyanide (50 g/l) TS, and examine the chromatogram in daylight. The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity with that obtained with solution B.
C. To 5 mg add 1 mL of water, 1 mL of pyridine R, and 5 mg of 4-nitrobenzoyl chloride R and heat to boiling. While shaking, add 0.1 mL of sodium carbonate (200 g/l) TS; an orange or amber colour is produced.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 44 mg/mL solution in aluminium chloride TS and calculate with reference to the anhydrous substance; 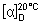 = -25° to -28°.
= -25° to -28°.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 10 μg/g.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method. Method A, using about 0.2 g of the substance; the water content is not less than 100 mg/g and not more than 130 mg/g.
Acidity. Dissolve 1.0 g in 100 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R with the aid of heat and titrate with sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS, methyl red/ethanol TS being used as indicator; not more than 0.5 mL is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (orange).
3-O-Methyl derivative. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using cellulose R2 as the coating substance and a mixture of 65 volumes of 1-butanol R, 15 volumes of glacial acetic acid R, and 25 volumes of water as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate (A) 10 μl of a 10 mg/mL solution of the test substance dissolved in a mixture of 4 volumes of hydrochloric acid (~250 g/l) TS and 96 volumes of methanol R, (B) 10 μl of a 50 μg/mL solution of (-)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylalanine RS, and (C) 20 μl of a mixture of equal volumes of solutions A and B. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in a current of warm air, and spray with a mixture of 5 volumes of a 0.05 g/mL solution of sodium nitrite R and 45 volumes of a 3 mg/mL solution of 4-nitroaniline R dissolved in a mixture of 80 volumes of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/l) TS and 20 volumes of water. Dry in a current of warm air, spray with sodium carbonate (75 g/l) TS, and examine the chromatogram in daylight. The spot obtained with solution B is more intense than any spot, corresponding in position and appearance, obtained with solution A. The test is valid only if the chromatogram obtained with solution C shows two distinctly separated spots.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.20 g, accurately weighed, in 20 mL of glacial acetic acid R1, add 20 mL of dioxan R, and titrate with perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method A. Each mL of perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 21.12 mg of C10H13NO4.