Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Misoprostol (Misoprostolum)
Molecular formula. C22H38O5
Relative molecular mass. 382.5
Graphic formula
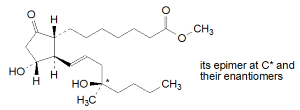
Chemical name
methyl rac-(13E,16RS)-11α,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprost-13-en-1-oate (mixture of 4 stereoisomers); mixture of methyl rac-7-{(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate and methyl rac-7-{(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4S)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate; CAS Reg. No. 59122-46-2.
Description. Clear, colourless or yellowish, oily liquid.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water R, soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS, sparingly soluble in acetonitrile R.
Category. Prostaglandin (PGE1) analogue.
Storage. Misoprostol neat oil should be kept in a tightly sealed container and stored at a temperature between -25 °C and -10 °C.
Additional information. Misoprostol is hygroscopic. It gradually degrades at room temperature, the degradation being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Misoprostol contains not less than 96.5% and not more than 102.0% of C22H38O5 with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
Either test A or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from misoprostol RS or with the reference spectrum of misoprostol.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography using silica gel R3 as the coating substance and a mixture of 8 volumes of toluene R, 2 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 1 volume of dehydrated ethanol R and 0.1 volume of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase, prepared immediately before use. Apply separately to the plate 100 μL of each of the following two solutions in dehydrated ethanol R. For solution (1) use 0.1 mg of the test substance per mL. For solution (2) use 0.1 mg of misoprostol RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in air, expose it to the vapour of iodine R and examine the chromatogram in daylight.
The principal spot obtained with solution (1) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity to that obtained with solution (2).
C. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the conditions given under “Assay”. The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained from solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to misoprostol in the chromatogram obtained from solution (2).
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, method A, using 1.0 mL of a 10 mg per mL solution of the test substance in dehydrated methanol R; the water content is not more than 10 mg/g.
Related substances
Prepare fresh solutions and perform the tests without delay.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.4 High performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel (5 μm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
mobile phase A: mix 28 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R with 69 volumes of water R and 3 volumes of methanol for chromatography R;
mobile phase B: mix 47 volumes of acetonitrile for chromatography R with 50 volumes of water R and 3 volumes of methanol for chromatography R.
|
|
Mobile phase A (% v/v) |
Mobile phase B (% v/v) |
Comment |
|
0–5 |
100 |
0 |
isocratic |
|
5–15 |
100 to 65 |
0 to 35 |
linear gradient |
|
15–(tr + 1) |
65 |
35 |
isocratic |
|
(tr + 1)–(tr + 4) |
65 to 0 |
35 to 100 |
linear gradient |
|
(tr + 4)–(tr + 9) |
0 |
100 |
isocratic |
|
(tr + 9)–(tr + 11) |
0 to 100 |
100 to 0 |
linear gradient |
|
(tr + 11)–(tr + 19) |
100 |
0 |
re-equilibration |
tr = retention time of misoprostol determined with solution (1)
Maintain the column temperature at 35 °C.
Prepare the following solutions using a mixture of 31 volumes of acetonitrile R and 69 volumes of water R as solvent. For solution (1) dissolve about 50 mg of the test substance in 10.0 mL and sonicate for about 10 minutes. Ensure that the temperature of the sonication bath is below room temperature to avoid degradation of misoprostol. For solution (2) dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 500 volumes. For solution (3) heat 5 mL of solution (1) in a water bath at 75 °C for 1 hour.
Operate with a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 200 nm.
Inject 20 µL of solution (3). The test is not valid unless the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 5.0, where Hp is the height above the extrapolated baseline of the peak due to impurity A (with a relative retention of about 0.95 with reference to misoprostol (retention time about 21 minutes)) and Hv is the height above the extrapolated baseline at the lowest point of the curve separating the peak due to impurity A from the peak due to misoprostol.
Inject alternately 20 μL each of solutions (1) and (2).
The chromatogram obtained with solution (1) may show the following impurities at the following relative retentions with reference to misoprostol (retention time about 21 minutes): impurity E (1st peak): about 0.84; impurity E (2nd peak): about 0.86; impurity B (1st peak): about 0.90; impurity B (2nd peak): about 0.92; impurity A: about 0.95; impurity D: about 1.27; impurity C: about 1.37. Use also the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) to identify impurity A and C.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the sum of the areas of any peak corresponding to impurity A, B and E is not greater than 7.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.5%);
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity C, when multiplied by a correction factor of 0.76, is not greater than 0.75 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.15%);
- the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.1%);
- the sum of the corrected area of any peak corresponding to impurity C and the areas of all other peaks, other than the principal peak, is not greater than 10 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (2.0%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Diastereoisomers
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.4 High performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (15 cm × 2.1 mm) packed with hybrid organic silica gel for chromatography R (3.5 μm). As the mobile phase use a mixture of 4 volumes of 2-propanol R, 96 volumes of heptane R and 0.1 volume of trifluoroacetic acid R.
As the test solution use 1.0 mg of the test substance per mL of a mixture of 4 volumes of 2-propanol R and 96 volumes of heptane R.
Maintain the column temperature at 25 °C.
Operate with a flow rate of 0.5 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 205 nm. Store the samples at 4 °C during analysis using a cooled autosampler.
Inject 10 µL of the test solution.
The chromatogram shows two principal peaks due to misoprostol at retention times of about 14 and 16 minutes. The test is not valid unless the resolution between these two peaks is at least 2.0.
Measure the areas of the two peaks corresponding to misoprostol. The first peak of misoprostol is 45%–55% of the sum of the areas of the two peaks due to misoprostol.
Assay
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.4 High performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel (5 μm). As the mobile phase use a mixture of 45 volumes of acetonitrile R and 55 volumes of water.
Prepare the following solutions in the mobile phase. For solution (1) use 0.1 mg of misoprostol per mL. For solution (2) use 0.1 mg of misoprostol RS per mL.
Maintain the column temperature at 35 °C.
Operate with a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 200 nm. Store the samples at 4 °C during analysis using a cooled autosampler.
Inject alternately 20 μL each of solutions (1) and (2). The test is not valid unless the symmetry factor of the peak due to misoprostol is between 0.8 and 1.5.
Measure the areas of the peak responses obtained in the chromatograms from solutions (1) and (2) and calculate the percentage content of misoprostol (C22H38O5), using the declared content of C22H38O5 in misoprostol RS.
Impurities
|
|
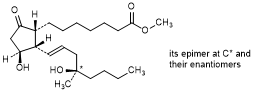
A. Methyl rac-(13E,16RS)-11β,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxo-12α-prost-13-en-1-oate (mixture of 4 stereoisomers); mixture of methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate and methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S,3S)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4S)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate; 8-epi-misoprostol
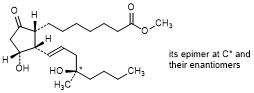
B. Methyl rac-(13E,16RS)-11α,16-dihydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxo-12α-prost-13-en-1-oate (mixture of 4 stereoisomers); mixture of methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate and methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4S)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate; 12-epi-misoprostol (synthesis impurity)
|
|
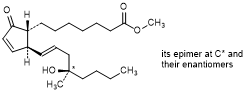
C. Methyl rac-(13E,16RS)-16-hydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprosta-10,13-dien-1-oate (mixture of 4 stereoisomers); mixture of methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S)-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopent-3-en-1-yl}heptanoate and methyl rac-7-{(1R,2S)-2-[(1E,4S)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopent-3-en-1-yl}heptanoate; misoprostol A
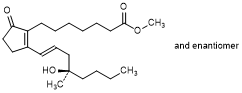
D. Methyl rac-(13E,16R)-16-hydroxy-16-methyl-9-oxoprosta-8(12),13-dien-1-oate; methyl rac-7-{2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4-methyloct-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopent-1-en-1-yl}heptanoate; misoprostol B
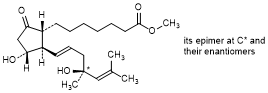
E. Methyl rac-(13E,16RS)-11α,16-dihydroxy-16,18-dimethyl-9-oxo-20-norprosta-13,17-dien-1-oate (mixture of 4 stereoisomers); mixture of methyl rac-7-{(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4R)-4-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylhept-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate and methyl rac-7-{(1R,2R,3R)-3-hydroxy-2-[(1E,4S)-4-hydroxy-4-methylhept-1-en-1-yl]-5-oxocyclopentyl}heptanoate