Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Nitrofurantoin (Nitrofurantoinum)
Nitrofurantoin, anhydrous
Nitrofurantoin monohydrate
Molecular formula. C8H6N4O5 (anhydrous); C8H6N4O5,H2O (monohydrate).
Relative molecular mass. 238.2 (anhydrous); 256.2 (monohydrate).
Graphic formula.
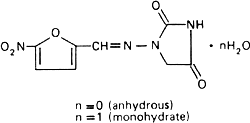
Chemical name. 1-[(5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino]hydantoin; 1-[[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)methylene]amino]-2,4-imidazolidinedione; CAS Reg. No. 67-20-9 (anhydrous).
1-[(5-Nitrofurfurylidene)amino]hydantoin monohydrate; 1-[[(5-nitro-2-furanyl)-methylene]amino]-2,4-imidazolidinedione monohydrate; CAS Reg. No. 17140-81-7 (monohydrate).
Other name. Furadoninum.
Description. Lemon-yellow crystals or a yellow, crystalline powder; odourless or almost odourless.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; very slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; soluble in dimethylformamide R.
Category. Antibacterial drug.
Storage. Nitrofurantoin should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light, and stored at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Nitrofurantoin should state whether the substance is the monohydrate or is in the anhydrous form.
Additional information. Nitrofurantoin melts at about 271°C with decomposition. Nitrofurantoin and its solutions are discoloured by alkali and by exposure to light and are decomposed upon contact with metals other than stainless steel and aluminium.
Requirements
Definition. Nitrofurantoin contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C8H6N4O5, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either test A alone or tests B, C and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. For Nitrofurantoin monohydrate, the substance must be previously dried to constant weight at 105°C. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from nitrofurantoin RS or with the reference spectrum of nitrofurantoin.
B. Carry out the following operations in subdued light.
Prepare a blank solution by dissolving 3.6 g of sodium acetate R in 20 mL of water, adding 0.3 mL of glacial acetic acid R, and diluting with sufficient water to produce 200 mL. Dissolve 0.12 g in 50 mL of dimethylformamide R and add sufficient water to produce 1000 mL. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 100 mL with the blank solution prepared above. Measure the absorption spectrum of the resulting solution against 10 mL of the blank solution to which 0.05 mL of dimethylformamide R has been added. When observed between 220 nm and 400 nm, the absorption spectrum exhibits maxima at about 266 nm and 367 nm. The absorbances of a 1-cm layer at these wavelengths are about 0.32 and 0.46, respectively. The ratio of the absorbance at 367 nm to that at 266 nm is between 1.36 and 1.42.
C. Dissolve 0.2 g in a mixture of 10 mL of dimethylformamide R and 1 drop of glacial acetic acid R. To 0.5 mL of this solution add 2 mL of water, 0.15 mL of copper(II) sulfate (80 g/l) TS, and 0.2 mL of pyridine R; shake with 3 mL of chloroform R and allow the layers to separate; a green colour is produced in the chloroform layer.
D. Dissolve 5 mg in 5 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS; a deep yellow solution is produced, which becomes deep orange-red on standing.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; anhydrous Nitrofurantoin loses not more than 10 mg/g. Nitrofurantoin monohydrate loses not less than 50 mg/g and not more than 71 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R2 as the coating substance and a mixture of 90 volumes of nitromethane R and 10 volumes of methanol R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of each of 2 solutions: (A) dissolve 0.25 g of the test substance in a minimum volume of dimethylformamide R and dilute to 10 mL with acetone R; (B) dilute 1 mL of solution A to 100 mL with acetone R. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and heat it at 105°C for 5 minutes. Spray the warm plate with phenylhydrazine/hydrochloric acid TS, heat it again at 105°C for 10 minutes, and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm). Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.4 g, accurately weighed, in a mixture of 10 mL of dimethylformamide R and 10 mL of dioxan R, add 0.10 mL of thymol blue/dimethylformamide TS and titrate with lithium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS to a dark green end-point, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method B. Each mL of lithium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 23.82 mg of C8H6N4O5.