Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Pyrimethamine (Pyrimethaminum)
Molecular formula. C12H13ClN4
Relative molecular mass. 248.7
Graphic formula.
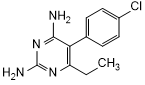
Chemical name. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethylpyrimidine-2,4-diamine (IUPAC), 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethyl-2,4-pyrimidinediamine (CAS), CAS Reg. No. 58-14-0.
Description. An almost white, crystalline powder or colorless crystals.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and acetone R.
Category. Antimalarial.
Storage. Pyrimethamine should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional Information. Pyrimethamine exhibits polymorphism.
Requirements
Definition. Pyrimethamine contains not less than 99.0% and not more than 101.0% of C12H13ClN4, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests.
- Either test A or test B may be applied.
-
Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained with pyrimethamine RS or with the reference spectrum of pyrimethamine.
If the spectra thus obtained are not concordant, repeat the test using the residues obtained by separately dissolving the test substance and pyrimethamine RS in a small amount of dehydrated ethanol R and evaporating to dryness. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from pyrimethamine RS.
-
Carry out test B.1 or, where a diode array detector is available, test B.2.
B.1 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the conditions given under the "Related Substances" with the following modifications. Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1), use solution (1) as described under "Related Substances". For solution (2), dissolve 12.5 mg pyrimethamine RS in about 20 mL solvent solution, sonicate for 10 minutes and dilute to 100.0 mL with mobile phase. Inject 30 μL of solutions (1) and (2). The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak corresponding to pyrimethamine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
The absorption spectrum (1.6) of a 15 μg/mL solution of the test substance in hydrochloric acid (0.005 mol/L) VS, when observed between 210 nm and 400 nm, corresponds to the spectrum obtained from pyrimethamine RS.
B.2. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the conditions given under the "Identity test B.1" with the following modifications. Record the UV spectrum of the principle peak in the chromatogram with a diode array detector in the range of 210 nm to 400 nm. The retention time and the UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) correspond to the retention time and the UV spectrum of the peak corresponding to pyrimethamine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
Sulfates. Shake 1.0 g with 50 mL of distilled water for 2 minutes and filter. Proceed with the filtrate as described under 2.2.2 Limit test for sulfates; the sulfate content is not more than 0.08 mg/g.
Sulfated Ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry at 105 °C for 4 hours; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Acidity or alkalinity. Boil 0.3 g with 15 mL of water, cool and filter. Add 0.25 mL of methyl red/ethanol TS to the filtrate; a yellow colour is observed. Not more than 0.1 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.05 mol/L) VS is required to change the colour of the solution to red.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (10 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (3.5 µm).
Prepare an ammonia solution by adding 10.0 mL of ammonia (~260 g/L) TS to 150 mL of water R, mix and dilute to 200.0 mL with water R. Prepare an ammonium bicarbonate buffer pH 9.3 by dissolving 0.8 g of ammonium bicarbonate R in 1500 mL of water, adjust the pH to 9.3 by adding the ammonia solution (about 25 mL), mix and dilute to 2000.0 mL with water R.
As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 55 volumes of ammonium bicarbonate buffer pH 9.3 and 45 volumes of methanol R.
Operate with a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 280 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 35 °C.
Prepare as a solvent solution a mixture of 50 volumes of acetic acid (~ 10 g/L) TS and 50 volumes of methanol R.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1), weigh 25 mg of the test substance into a 20 mL volumetric flask. Add approximately 15 mL of the solvent solution and sonicate for about 10 minutes. Dilute to volume with the solvent solution and mix. Dilute 5.0 mL of the filtrate to 50.0 mL with mobile phase. For solution (2), dilute 10.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL with mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with mobile phase. For solution (3), prepare 20 mL of a 1.25 mg/mL solution of pyrimethamine RS in sulfuric acid (~570 g/L) TS in a 25 mL conical flask. Heat the solution on a hotplate until it boils. Continue to heat to reduce the volume to about half its initial volume. The final solution should be clear with a light tinge of yellow. Cool and dilute 1 volume of this solution to 10 volumes with mobile phase.
Inject 30 μL of solution (3).
Record the chromatogram for about 2.5 times the retention time of pyrimethamine (retention time about 12 minutes). The impurities are eluted, if present, at the following relative retention with reference to the pyrimethamine: impurity A about 0.35; impurity B about 0.45; impurity C about 0.64; impurity D about 0.15; impurity E about 0.42; impurity F about 0.52 and impurity G about 2.28. The test is not valid unless in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the resolution between impurities A and B is at least 3.0.
Inject alternately 30 μL of solutions (1) and (2).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) to identify the peaks due to the impurities A, B and C.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
The area of any impurity peak is not greater than the area of the peak due to pyrimethamine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.10%).
-
The sum of the areas of all impurities is not greater than three times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.3%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.5 times the area of the peak due to pyrimethamine obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Assay. Dissolve 0.200 g in 30 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R, heating gently. Cool and titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS as described under 2.6. Non-aqueous titration, Method A, determining the end-point potentiometrically. Each mL of perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 24.87 mg of C12H13ClN4.
Impurities.
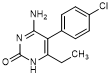
A. 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one (degradation product).
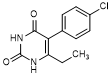
B. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione (degradation product).
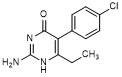
C. 2-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-ethylpyrimidin-4(1H)-one (degradation product).
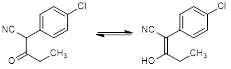
D. 2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-oxopentanenitrile and/or (2Z)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxypent-2-enenitrile (synthesis-related impurity).
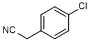
E. 2-(4-chlorophenyl)acetonitrile (synthesis-related impurity).
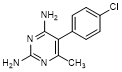
F. 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-6-methylpyrimidine-2,4-diamine (synthesis-related impurity).
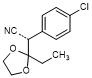
G. (2S)-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-2-(2-ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)acetonitrile (synthesis-related impurity).