Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Retinol concentrate, oily form (Retinolum densatum oleosum)
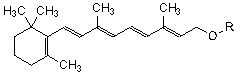
| Substance | R | Molecular Formula | Mr |
| all-(E)-retinol acetate | CO-CH3 | C22H32O2 | 328.5 |
| all-(E)-retinol propionate | CO-C2H5 | C23H34O2 | 342.5 |
| all-(E)-retinol palmitate | CO-C15H31 | C36H60O2 | 524.9 |
Chemical name. ester or mixture of esters (acetate (CAS Reg. No. 127-47-9), propionate (CAS Reg. No. 7069-42-3), or palmitate (CAS Reg. No. 79-81-2)) of all-(E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-ol.
Other name. Vitamin A concentrate (oily form).
Description. A yellow to brownish yellow, oily liquid.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; soluble or partly soluble in dehydrated ethanol R; miscible with organic solvents.
Category. Vitamin.
Storage. The oily form of Retinol concentrate should be kept in a well-closed and well-filled container, protected from light. Once the container has been opened its contents should be used as soon as possible; any part of the contents not used at once should be protected by an atmosphere of inert gas.
Labelling. The designation on the container should state the name of the retinol ester or esters, and their quantities expressed as the content of vitamin A in International Units (IU) per gram, whether any stabilizing agents are added and their quantities, as well as the method of restoring the solution if partial crystallization has occurred.
Additional information. Even in the absence of light the oily form of Retinol concentrate is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Partial crystallization may occur in concentrated solutions and upon refrigeration.
Requirements
Definition. The oily form of Retinol concentrate consists of an ester or a mixture of esters (acetate, propionate, or palmitate) of retinol, usually prepared by synthesis. It may be diluted in a suitable vegetable oil. It may contain suitable antimicrobial agents and stabilizing agents (such as vitamin E or other antioxidants).
The declared content of vitamin A is not less than 500 000 IU/g. Retinol concentrate contains not less than 95.0% and not more than 110.0% of the amount of vitamin A stated on the label.
Carry out the analytical procedures as rapidly as possible, avoiding exposure to actinic light and oxidizing agents, oxidizing catalysts (e.g. copper, iron, etc.), acids, heat and maintaining whenever possible an atmosphere of nitrogen above the solutions.
Identity tests
• Ether test A and B or tests A and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 12 volumes of cyclohexane R and 1 volume of ether R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 2 μl of each of the following solutions in cyclohexane R. For solution (A) dissolve a quantity of the Retinol concentrate containing the equivalent of 50 000 IU of vitamin A in 10 mL. For solution (B) prepare a solution of retinol esters RS containing the equivalent of 5000 IU of vitamin A per mL of each ester (retinol acetate, retinol propionate and retinol palmitate). After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in air and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot or spots obtained with solution (A) correspond(s) in position and appearance to one or more of the spots obtained with solution (B). The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (B) shows three clearly separated spots. The chromatogram of solution (A) shows the individual spot or spots of the corresponding ester or esters as stated on the label. The Rf values of the esters increase in the following order: retinol acetate, retinol propionate, retinol palmitate.
B. See the test described below under Assay, Method B. The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. To a quantity of the Retinol concentrate containing the equivalent of 50 000 IU of vitamin A, add 100 mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS. Dilute 1 mL of the resulting solution to 50 mL with a mixture of 100 volumes of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and 1 volume of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/l) TS. Immediately after preparation measure the absorbance (1.6) in the range 300–400 nm. The solution exhibits a single maximum at 326 nm. Heat the solution in a water-bath for 30 seconds and cool rapidly. The absorption spectrum of the resulting solution, when observed between 300 and 400 nm, exhibits a shoulder at 332 nm and maxima at 348, 367 and 389 nm.
Acid value (4.6). Not more than 2.0.
Peroxides. For solution (A) dissolve 0.30 g of the Retinol concentrate in 25 mL of a mixture of 4 volumes of methanol R and 6 volumes of toluene R. For solution (B) prepare a solution containing 0.27 g of ferric chloride R per mL and add 1.0 mL to 99 mL of a mixture of 4 volumes of methanol R and 6 volumes of toluene R. Dilute 2.0 mL to 100 mL with the same solvent mixture.
Place in 2 separate test-tubes in the following order, mixing after each addition, 3 mL of a solution containing 18 mg of ammonium thiocyanate R per mL, 10 mL of methanol R, 0.3 mL of ferrous sulfate/hydrochloric acid TS and 15 mL of toluene R. Then add 1.0 mL of solution (A) into one tube and 1.0 mL of solution (B) into the other, shake and allow to stand for 5 minutes. The colour produced with solution (A) is not more intense than that produced with solution (B).
Assay
• Either method A, where valid, or B may be applied.
A. Immediately dissolve a quantity of Retinol concentrate containing the equivalent of about 200 000 IU of vitamin A, accurately weighed, in 5 mL of n-pentane R and dilute with 2-propanol R to a presumed concentration of 10–15 IU per mL. Verify that the absorption maximum of the solution to be examined, against 2-propanol as blank, lies between 325 nm and 327 nm. Measure the absorbances at 300 nm, 326 nm, 350 nm and 370 nm. Calculate the ratio Aλ/A326 for each wavelength. If the ratios do not exceed 0.60 at 300 nm, 0.54 at 350 nm, and 0.14 at 370 nm, calculate the content of vitamin A in IU per g from the expression: A326 × V × 1900 / (100 × m), where A326 is the absorbance at 326 nm, V is the dilution factor used to give 10–15 IU per mL, m is the mass of sample used in g and 1900 is the factor to convert the specific absorbances of esters of retinol into IU per g.
If one or more of the ratios Aλ/A326 exceeds the values given, or if the wavelength of the absorption maximum does not lie between 325 nm and 327 nm, use Method B.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (15 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with octadecysilyl groups (5 μm). As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 95 volumes of methanol R and 5 volumes of water R.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) transfer a quantity of Retinol concentrate containing the equivalent of about 100 000 IU of vitamin A, accurately weighed, into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Dissolve immediately in 5 mL of n-pentane R. Add 40 mL of 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide TS in 2-propanol R. Swirl gently and allow the mixture to stand for 10 minutes at a temperature between 60 °C and 65 °C, swirling occasionally. Allow to cool to room temperature, dilute to volume with 2-propanol R containing 1 g/l butylated hydroxytoluene R and homogenize carefully to avoid air-bubbles. Dilute 5 mL of the resulting solution to 50 mL with 2-propanol R. For solution (2) transfer an amount of retinol acetate RS containing the equivalent of about 100 000 IU of vitamin A, accurately weighed, into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Proceed as described for solution (1).
Operate with a flow rate of 1 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 325 nm.
Inject separately 10 µl each of solutions (1) and (2) and record the chromatograms for 1.5 times the retention time of retinol.
Measure the areas of the peak responses obtained in the chromatograms from solutions (1) and (2) and calculate the content of vitamin A in IU per g.