Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Rifampicin (Rifampicinum)
Graphic formula.
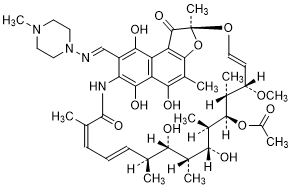
Molecular formula. C43H58N4O12
Relative molecular mass. 822.9.
Chemical name. (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-5,6,9,17,19-pentahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-8-[[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)imino]methyl]-1,11-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-21-yl acetate (IUPAC); 3-[[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)imino]methyl]rifamycin (CAS).
CAS Registry Number. 13292-46-1.
Other name. Rifampin.
Description. A reddish-brown or brownish-red, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Slightly soluble in water R; soluble in methanol R; slightly soluble in acetone R and ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Category. Antileprosy; antituberculosis medicine.
Storage. Rifampicin should be kept in a tightly closed container or in an atmosphere of nitrogen, protected from light, not exceeding 25 °C.
Additional information. Rifampicin exhibits polymorphism.
Requirements
Definition. Rifampicin contains not less than 97.0% and not more than 102.0% of C43H58N4O12, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Manufacture. The production method is validated to demonstrate that thesuspectedcarcinogenic nitrosamine 1-methyl-4-nitroso piperazine (MeNP) is eliminated or minimized and adequately controlled in the final product in line with the responsible regulatory authority’s requirements. A suitable method to determine MeNP in Rifampicin active pharmaceutical ingredient or Rifampicin tablets and capsules can be found in the Supplementary Section of The International Pharmacopoeia under Test methods used during development or manufacture.
Identity tests
- Either tests A, B and D or tests B, C and D may be applied.
-
Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from rifampicin RS or with the reference spectrum of rifampicin.
If the spectra thus obtained are not concordant, repeat the test using the residues obtained by separately dissolving the test substance and rifampicin RS in a small amount of dichloromethane R and evaporating to dryness. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from rifampicin RS.
-
Dissolve 50 mg of the test substance in 50 mL of methanol R and dilute 1 mL of this solution to 50 mL with phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, TS. The absorption spectrum of the resulting solution, when observed between 220 nm and 500 nm, exhibits 4 maxima at about 237 nm, 254 nm, 334 nm and 475 nm; the ratio of the absorbance of a 1 cm layer at the maximum at about 334 nm to that at the maximum at about 475 nm is about 1.75.
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a freshly prepared mixture of ethyl acetate R, ammonia (~260 g/L) TS, ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and cyclohexane R (20:9:4.5:5 V/V) as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 µL of each of the following 2 solutions in methanol R containing (A) 1.0 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 1.0 mg of rifampicin RS per mL. Develop the plate. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air or in a current of air. Examine the chromatogram under ultraviolet light (254 nm). The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (A) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity with the spot due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (B).
-
Suspend 25 mg of the test substance in 25 mL of water R, shake for 5 minutes and filter. To 5 mL of the filtrate, add 1 mL of ammonium persulfate/phosphate buffer TS and shake for a few minutes; the colour turns from orange-yellow to violet-red without the formation of a precipitate.
Heavy metals (2.2.3). Place 1.0 g in a silica crucible and mix it with 4 mL of magnesium sulfate/sulfuric acid TS. Heat cautiously to ignition and continue heating until a white or, at most, greyish residue is obtained. Ignite at a temperature not exceeding 800 °C, allow to cool, and moisten the residue with a few drops of sulfuric acid (~100 g/L) TS. Evaporate, ignite again, and allow to cool. Next, dissolve the residue in hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS, add, drop by drop, a solution of ammonia (~100 g/L) PbTS, until the pH of the solution is between 8 and 8.5, then add, also drop by drop, acetic acid (~60 g/L) Pb TS to adjust the pH to 3–4, filter, dilute with water to 40 mL and mix. Determine the heavy metals content as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 1.0 mg/g, determined on 2.0 g.
Loss on drying. Dry 1.000 g of the test substance at 80 °C under reduced pressure (not exceeding 0.6 kPa or about 5 mm of mercury) for 4 hours; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
pH value (1.13). Shake 0.10 g with 10 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R; pH of the suspension, 4.5–6.5.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (4.6 mm x 12 cm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octylsilyl groups (5 µm).
As the mobile phase, use a mixture of 35 volumes of acetonitrile R and 65 volumes of a solution containing 0.1 % (V/V) of phosphoric acid (~1440 g/L) TS, 1.9 g/L of sodium perchlorate R, 5.9 g/L of citric acid R and 20.9 g/L of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R.
Operate with a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 254 nm.
Prepare as a solvent solution, a mixture of 10 volumes of a 210.1 g/L solution of citric acid R, 23 volumes of a 136.1 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R, 77 volumes of a 174.2 g/L solution of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R, 250 volumes of acetonitrile R and 640 volumes of water R.
Prepare the following solutions immediately before use: for solution (1), dissolve 20.0 mg of the test substance in acetonitrile R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with the solvent solution. For solution (2), dissolve 20.0 mg of rifampicin quinone RS (impurity A) in acetonitrile R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. To 1.0 mL of this solution, add 1.0 mL of solution (1) and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture. For solution (3), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 100.0 mL.
Inject 20 µL each of solutions (1), (2) and (3). Record the chromatogram for about twice the retention time of rifampicin.
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2), the resolution between the peaks due to rifampicin and impurity A is at least 4.0. The test is also not valid unless the signal-to-noise ratio of the peak due to rifampicin obtained with solution (3) is at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A,is not greater than 1.5 times the area of the peak due to impurity A in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.5 %);
-
the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0 %).
-
The sum of the areas ofall impurity peaks, other than impurity A, is not greater than 3.5 times the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (3.5%). Disregard any peak with an area of less than the area of the peak due to rifampicin in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.05%).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.100 g in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, TS. Measure the absorbance of the resulting solution as described under 1.6 Spectrophotometry in the visible and ultraviolet regions in a cuvette or cell with an optical pathlength of 10 mm layer at about 475 nm, using as the blank phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, TS. Calculate the content of C43H58N4O12, using the absorptivity value of 18.7 ( = 187).
= 187).
Impurities
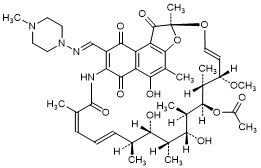
A. (2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-5,17,19-Trihydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-8-{(E)-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)imino]methyl}-1,6,9,11-tetraoxo-1,2,6,9-tetrahydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-21-yl acetate; Rifampicin quinone,
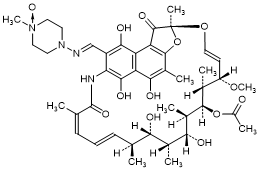
B. 1-[(E)-{[(2S,12Z,14E,16S,17S,18R,19R,20R,21S,22R,23S,24E)-21-(Acetyloxy)-5,6,9,17,19-pentahydroxy-23-methoxy-2,4,12,16,18,20,22-heptamethyl-1,11-dioxo-1,2-dihydro-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienoimino)naphtho[2,1-b]furan-8-yl]methylidene}amino]-4-methylpiperazine N1-oxide; Rifampicin N-oxide.