Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Thiopental sodium (Thiopentalum natricum)
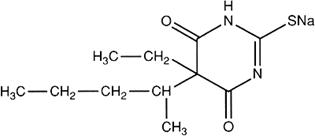
C11H17N2NaO2S
Relative molecular mass. 264.3
Chemical name. Sodium 5-ethyl-5-(1-methylbutyl)-2-thiobarbiturate; 5-ethyldihydro-5-(1-methylbutyl)-2-thioxo-4,6(1H,5H)-pyrimidinedione monosodium salt; CAS Reg. No. 71-73-8.
Description. A yellowish white powder; odour, characteristic.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water and ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. General anaesthetic.
Storage. Thiopental sodium should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Thiopental sodium is hygroscopic. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Thiopental sodium contains not less than 97.0% and not more than the equivalent of 102.0% of C11H17N2NaO2S, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and D or tests B, C, and D may be applied.
A. Place about 0.5 g in a separatory funnel, add 10 mL of water and acidify with hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS. Shake with 20 mL of ether R, separate the ether layer, wash with 10 mL of water, dry over anhydrous sodium sulfate R, and filter. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness over a water-bath and dry the residue at 100 - 105 °C. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from thiopental RS or with the reference spectrum of thiopental.
B. See the test described below under "Related substances". Apply 10μl of each of solutions B and C to the plate and develop the chromatogram for a distance of 18 cm. The principal spot obtained with solution B corresponds in position and intensity with that obtained with solution C.
C. Fuse 0.2 g with 1 g of sodium hydroxide R in a test-tube until the glass glows red; the melt turns red-brown and vapours are evolved. Insert moistened pH-indicator paper R into the vapours; its coloration is changed to an alkaline range. Cool and add 5 mL of water to the melt, mix well, and filter. Acidify the filtrate with sulfuric acid (~100 g/l) TS and heat gently; the vapours evolved turn a strip of lead nitrate paper R to brown and then to black.
D. When tested for sodium as described under 2.1 General identification tests, yields the characteristic reactions. If reaction B is to be used, prepare a 20 mg/mL solution.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 1 g in 10 mL of water is clear and not more intensely coloured than standard colour solution Gn5 when compared as described under 1.11.1 Colour of liquids.
Loss on drying. Dry at 80 °C for 4 hours; it loses not more than 20 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R4 as the coating substance and the lower layer of a mixture of 5 volumes of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, 15 volumes of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, and 80 volumes of chloroform R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 20μl of each of three solutions containing (A) 10 mg of Thiopental sodium per mL (disregard any slight residue), for solution (B) dilute 1 mL of solution A to 10 mL, for solution (C) dissolve 85 mg of thiopental RS in 10 mL of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS and dilute with sufficient water to produce 100 mL, and for solution (D) dilute 0.5 mL of solution A to 100 mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, examine the chromatogram immediately in ultraviolet light.
Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution D (0.5%). Disregard any spot at the point of application.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.15 g, accurately weighed, in 5 mL of water, add 2 mL of sulfuric acid (~100 g/l) TS, and extract with four 10-mL quantities of chloroform R. Filter the combined chloroform extracts, evaporate the filtrate to dryness on a water-bath, and dissolve the residue in 30 mL of dimethylformamide R previously neutralized with lithium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS. Titrate immediately with lithium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS, using 0.1 mL of thymol blue/methanol TS as indicator, until a blue colour is obtained. Protect the solution from atmospheric carbon dioxide during the titration.
Each mL of lithium methoxide (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 26.43 mg of C11H17N2NaO2S.