Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Warfarin sodium (Warfarinum natricum)
Molecular formula. C19H15NaO4; C19H15NaO4,C3H8O,H2O (hyclate).
Relative molecular mass. 330.3; 408.4 (hyclate).
Graphic formula.
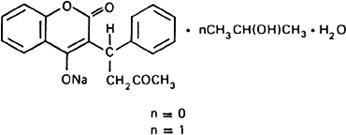
Chemical name. 3-(α-Acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt; 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-2-one sodium salt; CAS Reg. No. 129-06-6.
3-(α-Acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt compound with 2-propanol monohydrate; 4-hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)-2H-benzopyran-2-one sodium salt 2-propanol monohydrate.
Description. A white, amorphous or crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Soluble in less than 1 part of water and in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; slightly soluble in ether R.
Category. Anticoagulant.
Storage. Warfarin sodium should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Warfarin sodium should state whether the substance is in the amorphous or the crystalline, clathrate form.
Additional information. Warfarin sodium is discoloured by light. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Warfarin sodium contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C19H15NaO4, calculated with reference to the anhydrous and 2-propanol-free substance.
Identity tests
A. Dissolve 0.1 g in 25 mL of water, add 0.1 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS, collect the precipitate on a filter (keep the filtrate for test C), wash with water, and dry the residue at 105 °C. Melting temperature, about 162 °C (warfarin). (Keep the residue for test B.)
B. Carry out the examination of the residue obtained in test A as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from warfarin RS or with the reference spectrum of warfarin.
C. The filtrate obtained in test A yields reaction B described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of sodium.
D. Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of water, add 5 mL of nitric acid (~1000 g/l) TS, and filter. To the filtrate add 2 mL of potassium dichromate (0.0167 mol/l) VS and shake for 5 minutes; only the clathrate yields a light greenish blue solution.
Clarity of solution. The opalescence of a solution of 0.50 g in 10 mL of carbon-dioxide-free water R is not more intense than that of opalescence standard TS2.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method, Method A, using about 0.4 g of the substance; the water content is not more than 45 mg/g.
pH value. pH of a 10 mg/mL solution in carbon-dioxide-free water R, 7.2-8.3.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R4 as the coating substance and a mixture of 5 volumes of chloroform R, 5 volumes of cyclohexane R, and 2 volumes of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 20 μl of each of 2 solutions in acetone R containing (A) 20 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.020 mg of the test substance per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and immediately examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm). Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Absorbance in alkaline solution. Dissolve 1.25 g, accurately weighed, in 10 mL of sodium hydroxide (50 g/l) TS, filter through a membrane filter, and, within 15 minutes, measure the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 385 nm against a solvent cell containing sodium hydroxide (50 g/l) TS; not more than 0.3.
2-Propanol content. Dissolve about 0.8 g, accurately weighed, in 25.0 mL of water. Add 25.0 mL of sulfuric acid (0.125 mol/l) VS while swirling, filter, and transfer 10 mL of the clear filtrate to a 250-mL flask containing 40 mL of water. Add some boiling chips, then 30 mL of potassium dichromate TS3, and connect the flask to a condenser by means of a 75° connecting tube. Distil 60 mL, collecting the distillate in 20 mL of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS contained in a 250-mL iodine flask immersed in an ice-bath. Add, with swirling, 20.0 mL of iodine (0.1 mol/l) VS, insert the stopper in the flask, and allow to stand for 30 minutes. Add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/l) TS through the well in the flask, rinse the well and the neck of the flask with water, swirl to mix, remove the stopper, and titrate the excess iodine with sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/l) VS, adding 3 mL of starch TS towards the end of the titration. Each mL of iodine (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 1.001 mg of 2-propanol. The amorphous substance contains not more than 3 mg per g and the crystalline clathrate contains between 43 and 83 mg of 2-propanol per g.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.1 g, accurately weighed, in sufficient sodium hydroxide (0.01 mol/l) VS to produce 100 mL and dilute 10 mL to 1000 mL with sodium hydroxide (0.01 mol/l) VS. Measure the absorbance of a 1-cm layer of the diluted solution at the maximum at about 308 nm. Calculate the amount of C19H15NaO4 in the substance being tested by comparison with warfarin RS, similarly and concurrently examined, taking into account that each mg of warfarin RS is equivalent to 1.071 mg of C19H15NaO4. In an adequately calibrated spectrophotometer the absorbance of the reference solution should be 0.47 ± 0.03.