Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Zinc acetate (Zinci acetas)
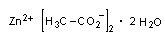
C4H6O4Zn . 2 H2O
Relative molecular mass. 219.5.
Chemical names. Zinc acetate dihydrate; Acetic acid, zinc salt, hydrate (2:1:2); CAS Reg. No. 5970-45-6.
Description. A white or almost white crystalline powder or flakes.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water; soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Adjunct to oral rehydration salts in (prevention and) treatment of dehydration due to diarrhoea; astringent.
Storage. Zinc acetate should be kept in a well-closed, non-metallic container.
Labelling. The designation on the container should state that the substance is in the dihydrate form.
Requirements
Definition. Zinc acetate dihydrate contains not less than 99.0% and not more than 101.0% of C6H6O4Zn,2H2O.
Identity tests
A. Dissolve 0.1 g in 5 mL of water R and add 0.2 mL of sodium hydroxide
(~400 g/l) TS. A white precipitate is formed. Add a further 2 mL of sodium hydroxide (~400 g/l) TS. The precipitate dissolves. Add 10 mL of ammonium chloride (~100 g/l) TS. The solution remains clear. Add 0.1 mL of sodium sulfide TS. A flocculent white precipitate is formed.
B. Dissolve 0.2 g in 4 mL of water R and add 4 mL of ferric chloride (65 g/l) TS. A red-brown colour is formed. Boil the solution; a red-brown precipitate is produced. Add drop wise sufficient hydrochloric acid (~250 g/l) TS to dissolve the precipitate; a yellow colour appears.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 1 g in 10 mL of water R is clear and colourless.
pH value (1.13). pH of a 0.05 g/mL solution in carbon-dioxide-free water R, 5.8–7.0.
Aluminum. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 1, at a wavelength of 309.3 nm using an aluminum hollow cathode lamp, an acetylene-nitrous oxide flame, and a slit width of 0.5 nm. Dissolve 2.5 g in 25 mL of cadmium-free and lead-free nitric acid (~200 g/l) TS. Use aluminum standard (10 μg Al/mL) TS to prepare the reference solutions; not more than 5 μg of Al per g.
Arsenic. Use a solution of 5.0 g in 50 mL of water R, add 10 mL of stannated hydrochloric acid (~250 g/l) AsTS, and proceed as described under 2.2.5 Limit test for arsenic; not more than 2 µg As per g.
Cadmium. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 1, at a wavelength of 228.8 nm using a cadmium hollow cathode lamp, an air-acetylene flame and a slit width of 0.5 nm. Dissolve 2.5 g in 25 mL of cadmium-free and lead-free nitric acid (~200 g/l) TS. Use cadmium standard (1000 μg Cd/mL) TS to prepare the reference solutions; not more than 2 μg of Cd per g.
Copper. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 1, at a wavelength of 324.8 nm using a copper hollow cathode lamp, an air-acetylene flame and a slit width of 0.5 nm. Dissolve 1.25 g in 25 mL of cadmium-free and lead-free nitric acid (~200 g/l) TS. Use copper standard (10 μg Cu/mL) TS to prepare the reference solutions; not more than 50 μg of Cu per g.
Chlorides. Dissolve 5.0 g in 25 mL of water R and proceed as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 50 µg/g.
Iron. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 1, at a wavelength of 248.3 nm using an iron hollow cathode lamp, an air-acetylene flame and a slit width of 0.2 nm. Dissolve 1.25 g in 25 mL of cadmium-free and lead-free nitric acid (~200 g/l) TS. Use iron standard FeTS to prepare the reference solutions; not more than 50 μg of Fe per g.
Lead. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 1, at a wavelength of 283.3 nm using a lead hollow cathode lamp, an air-acetylene flame and a slit width of 0.5 nm. Dissolve 5.0 g in 25 mL of cadmium-free and lead-free nitric acid (~200 g/l) TS. Use strong lead PbTS to prepare the reference solutions; not more than 10 μg of Pb per g.
Reducing substances. Dissolve 1 g in 100 mL of water R. Add 5 mL of sulfuric acid (~100 g/l) TS and 1.5 mL of potassium permanganate (~0.3 g/l) TS and boil for 5 minutes; the pink colour of the solution remains.
Sulfates. Dissolve 4.8 g in 25 mL of water R, and proceed as described under 2.2.2 Limit test for sulfates; the sulfate content is not more than 100 µg/g.
Assay
Dissolve about 100 mg, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of acetic acid (~10 g/l) TS and proceed with the titration as described under 2.5 Complexometric titrations for zinc. Each mL of disodium edetate (0.05 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 10.98 mg of C4H6O4Zn,2H2O.