Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Zinc gluconate (Zinci gluconas)
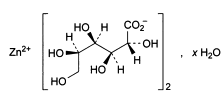
C12H22O14Zn . x H2O
Relative molecular mass. 455.7 (anhydrous).
Chemical names. Zinc bis(D-gluconate) hydrate; D-Gluconic acid, zinc salt, hydrate (2:1:?); CAS Reg. No. 1264109-00-3.
Description. White or almost white, hygroscopic, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Soluble in water; practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol.
Category. Adjunct to oral rehydration salts in (prevention and) treatment of dehydration due to diarrhoea; astringent.
Storage. Zinc gluconate should be kept in a tightly closed container.
Additional information. Zinc gluconate is a hygroscopic material, and should be protected from atmospheric moisture.
Requirements
Definition. Zinc gluconate contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C12H22ZnO14 calculated with reference to the anhydrous substance.
Identity tests
A. Dissolve 0.1 g in 5 mL of water R. Add 0.5 mL of potassium ferrocyanide (~53 g/l) TS. A white precipitate is formed that does not dissolve upon the addition of 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~330 g/l) TS.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R5 as the coating substance and a mixture of 10 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 50 volumes of water R and 40 volumes of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 1 μl of each of 2 solutions in water R containing (A) 10 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 10 mg of calcium gluconate R per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, heat the plate for 10 minutes at 105 °C. Spray with ammonium molybdate/ceric sulfate/sulfuric acid TS. Heat the plate for 10 minutes at 105 °C. Examine the chromatogram in daylight.
The principal spot obtained with solution A corresponds in position, appearance and intensity to that obtained with solution B.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 0.2 g in 10 mL of water R is clear and colourless.
pH value (1.13). pH of a 0.01 g/mL solution, 5.5–7.5.
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method , Method A. Use 0.250 g of the test substance. The water content is not more than 120 mg/g.
Cadmium. Determine by atomic absorption spectrophotometry 1.8 Atomic spectrometry: emission and absorption, Method 2, at a wavelength of 228.8 nm using a cadmium hollow cathode lamp, an air-acetylene flame and a slit width of 0.5 nm. Dissolve 1.25 g in 25 mL of water R. As a reference solution use cadmium standard (1000 μg Cd/mL) TS; not more than 2 μg of Cd per g.
Chlorides. Dissolve 0.5 g in 25 mL of water R, and proceed as described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 500 µg/g.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 4, not more than 10 µg/g, substituting acetic acid (~60 g/l) PbTS with hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS in all cases.
Reducing sugars. Dissolve 0.5 g in a mixture of 2 mL of hydrochloric acid (~330 g/l) TS and 10 mL of water R. Boil for 5 minutes, allow to cool, add 10 mL of sodium carbonate (~10 g/l) TS and allow to stand for 10 minutes. Dilute to 25 mL with water R and filter. To 5 mL of the filtrate add 2 mL of cupri-tartaric TS and boil for 1 minute. Allow to stand for 2 minutes; no red-brown precipitate is formed.
Sulfates. Dissolve 0.96 g in 25 mL of water R, and proceed as described under 2.2.2 Limit test for sulfates; the sulfate content is not more than 500 µg/g.
Microbial contamination. Determine as described under 3.3.1 Microbiological examination of non-sterile products: microbial enumeration tests. The acceptance criteria are: TAMC 103 CFU/g and TYMC 102 CFU/g.
Assay
Dissolve about 200 mg, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of acetic acid (~10 g/l) TS and proceed with the titration as described under 2.5 Complexometric titrations for zinc. Each mL of disodium edetate (0.05 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 22.78 mg of C12H22ZnO14.