Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Benzylpenicillin potassium (Benzylpenicillinum kalicum)
Benzylpenicillin potassium (non-injectable)
Benzylpenicillin potassium, sterile
Molecular formula. C16H17KN2O4S
Relative molecular mass. 372.5
Graphic formula.
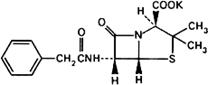
Chemical name. Potassium (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-(2-phenylacetamido)-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate; potassium [2S-(2α,5α,6β)]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[(phenylacetyl)amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate; CAS Reg. No. 113-98-4.
Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder; odourless or with a faint characteristic odour.
Solubility. Very soluble in water; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Antibiotic.
Storage. Benzylpenicillin potassium should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light, and stored at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Labelling. The designation sterile Benzylpenicillin potassium indicates that the substance complies with the additional requirements for sterile Benzylpenicillin potassium and may be used for parenteral administration or for other sterile applications.
Additional information. Benzylpenicillin potassium is moderately hygroscopic; it is readily decomposed by acids, alkalis and oxidizing agents. Even in the absence of light, Benzylpenicillin potassium is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Benzylpenicillin potassium contains not less than 96.0% and not more than 102.0% of C16H17KN2O4S, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and C or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from benzylpenicillin potassium RS or with the reference spectrum of benzylpenicillin potassium.
B. To 2 mg in a test-tube add 1 drop of water followed by 2 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS and mix; the solution is colourless. Immerse the test-tube for 1 minute in a water-bath; the solution remains colourless. Place 2 mg in a second test-tube, add 1 drop of water and 2 mL of formaldehyde/sulfuric acid TS and mix; the solution is brownish yellow. Immerse the test-tube for 1 minute in a water-bath; a reddish brown colour is produced.
C. Ignite a small quantity, dissolve the residue in water and filter; on addition of 2 mL of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS to the filtrate it yields the reaction described under 2.1 General identification tests, as characteristic of potassium.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 20 mg/mL solution; 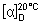 = +270° to +300°.
= +270° to +300°.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 0.20 g in 10 mL of water is clear and colourless.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
pH value. pH of a 20 mg/mL solution in carbon-dioxide-free water R, 5.0-7.5.
Light-absorbing impurities. Using a freshly prepared 1.9 mg/mL solution in water, measure the absorbances of a 1-cm layer at 280 nm and at 325 nm; the absorbance at each of these wavelengths does not exceed 0.10.
Assay. Dissolve about 50 mg, accurately weighed, in sufficient water to produce 1000 mL. Transfer two 2.0-mL aliquots of this solution into separate stoppered tubes. To one tube add 10.0 mL of imidazole/mercuric chloride TS, mix, stopper the tube and place in a water-bath at 60°C for exactly 25 minutes. Cool the tube rapidly to 20°C (solution A).
To the second tube add 10.0 mL of water and mix (solution B).
Without delay measure the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at the maximum at about 325 nm against a solvent cell containing a mixture of 2.0 mL of water and 10.0 mL of imidazole/mercuric chloride TS for solution A and water for solution B.
From the difference between the absorbance of solution A and that of solution B, calculate the amount of C16H17KN2O4S in the substance being tested by comparison with benzylpenicillin sodium RS similarly and concurrently examined, taking into account that each mg of benzylpenicillin sodium RS (C16H17N2NaO4S) is equivalent to 1.045 mg of benzylpenicillin potassium (C16H17KN2O4S). In an adequately calibrated spectrophotometer the absorbance of the reference solution should be 0.62 ± 0.03.
Additional Requirements for Benzylpenicillin Potassium for sterile use
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 0.01 IU of endotoxin RS per mg of benzylpenicillin.
Sterility. Complies with 3.2 Test for sterility.