Monographs: Dosage forms: Specific monographs: Sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine tablets (Sulfadoxini et pyrimethamini compressi)
Category. Antimalarial.
Storage. Sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine tablets should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Strength in the current WHO Model list of essential medicines: 500 mg sulfadoxine and 25 mg pyrimethamine.
Strength in the current WHO Model list of essential medicines for children: 500 mg sulfadoxine and 25 mg pyrimethamine.
Requirements
Comply with the monograph for "Tablets".
Definition. Sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine tablets contain Sulfadoxine and Pyrimethamine. They contain not less than 90.0% and not more than 110.0% of the amounts of sulfadoxine (C12H14N4O4S) and pyrimethamine (C12H13ClN4) stated on the label.
Identity tests
A. Carry out test A.1 or, where UV detection is not available, test A.2.
A.1 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 75 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 25 volumes of methanol R and 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of each of the following two solutions in methanol R. For solution (A) shake a quantity of the powdered tablets containing about 100 mg of Sulfadoxine for 5 minutes with 20 mL, filter and use the filtrate. For solution (B) use 5 mg of sulfadoxine RS and 0.25 mg of pyrimethamine RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in a current of air and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The two principal spots obtained with solution (A) correspond in position, appearance and intensity to those obtained with solution (B).
A.2 Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using the conditions described above under test A.1 but using silica gel R5 as the coating substance. Dip the plate in modified Dragendorff reagent TS. Examine the chromatogram in daylight.
The two principal spots obtained with solution (A) correspond in position, appearance and intensity to those obtained with solution (B) (the spot due to pyrimethamine is faintly visible).
B.See the test described under Assay. The retention times of the two principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) are similar to those in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4).
Dissolution
Carry out the test as described under 5.5 Dissolution test for solid oral dosage forms , using as the dissolution medium, 1000 mL of hydrochloric acid (~4 g/l) TS and rotating the paddle at 75 revolutions per minute. At 30 minutes withdraw a sample of about 5 mL of the medium through an in-line filter and use the filtrate. Determine the content of sulfadoxine (C12H14N4O4S) and pyrimethamine (C12H13ClN4) in the filtrate according to the method as described under Assay and preparing solution (4) under Assay as follows: dilute 10.0 mL of solution (2) and 2.0 mL of solution (3) to 20.0 mL with hydrochloric acid (~4 g/l) TS.
For each of the six tablets calculate the total amount of sulfadoxine (C12H14N4O4S) and pyrimethamine (C12H13ClN4) in the medium from the results obtained. For both substances the amount in solution for each tablet is not less than 80% of the amount declared on the label. For either substance, if the amount obtained for one of the six tablets is less than 80%, repeat the test using a further six tablets; the average amount for all 12 tablets tested is not less than 75% and no tablet releases less than 60%.
Sulfadoxine-related substances
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 μm).
As the mobile phase use a solution prepared as follows: dissolve 10 mL of glacial acetic acid R and 0.5 mL of triethylamine R in about 800 mL of water R, dilute to 1000 mL and adjust the pH to 4.2 by adding sodium hydroxide (~400 g/l) TS. Mix 850 mL of this solution with 120 mL of acetonitrile R and 30 mL of methanol R.
For solution (1) weigh and powder 20 tablets. Transfer a quantity of the powder containing about 200 mg of Sulfadoxine into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Add 35 mL of acetonitrile R and sonicate for about 10 minutes. Allow to cool to room temperature and make up to volume with mobile phase. Filter a portion of this solution through a 0.45 μm filter, discarding the first few mL of the filtrate. For solution (2) dilute 1 mL of solution (1) to 200 mL with the mobile phase.
For solution (3) prepare a solution containing about 1 mg of sulfadoxine RS and about 0.5 mg of sulfamethoxazole R per mL in acetonitrile R. Dilute 10 mL of this solution to 100 mL with the mobile phase.
Operate with a flow rate of 2 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 270 nm.
Inject separately 100 μl each of solutions (1), (2) and (3). Record the chromatograms for about 3.5 times the retention time of sulfadoxine (to ensure that pyrimethamine is eluted).
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) the following impurity peaks, if present, are eluted at the following relative retention with reference to sulfadoxine (retention time about 18 minutes): impurity A (sulfanilamide) about 0.1; impurity B about 0.2; impurity D about 0.3; impurity C about 1.4. A peak due to pyrimethamine has a relative retention of about 2.7. The test is not valid unless in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the resolution between the peaks due to sulfadoxine and to sulfamethoxazole (with relative retention of about 1.1 with reference to sulfadoxine) is at least 2.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) the area of any peak, other than the peaks due to sulfadoxine and to pyrimethamine, is not greater than the area of the peak due to sulfadoxine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%). The sum of the areas of all peaks, other than the peaks due to sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine, is not greater than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.05%).
Assay
• Either method A or B may be applied.
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 μm).
As the mobile phase use a solution prepared as follows: dissolve 10 mL of glacial acetic acid R and 0.5 mL of triethylamine R in about 800 mL of water R, dilute to 1000 mL and adjust the pH to 4.2 by adding sodium hydroxide (~400 g/l) TS. Mix 800 mL of this solution with 200 mL of acetonitrile R.
For solution (1) weigh and powder 20 tablets and transfer a quantity of the powder containing about 0.50 g of Sulfadoxine, accurately weighed, into a 200 mL volumetric flask. Add about 70 mL of acetonitrile R and sonicate for 10 minutes. Allow to cool to room temperature, make up to volume using the mobile phase and sonicate for 10 minutes. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 25 mL with the mobile phase and filter a portion of this solution through a 0.45 μm filter, discarding the first few mL of the filtered solution. For solution (2) transfer 25 mg of sulfadoxine RS, accurately weighed, to about 10 mL of acetonitrile R, sonicate until dissolved and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase. For solution (3) transfer 25 mg of pyrimethamine RS, accurately weighed, to about 35 mL of acetonitrile R, sonicate until dissolved and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. For solution (4) dilute 10.0 mL of solution (2) and 2.0 mL of solution (3) to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Operate with a flow rate of 2 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 227 nm.
Inject 20 µl of solution (4). The assay is not valid unless the resolution between the peaks due to sulfadoxine and to pyrimethamine, eluting in this order, is at least 5. The run time for the analyses is not less than 25 minutes.
Inject separately 20 µl each of solutions (1) and (4).
Measure the areas of the peak responses obtained in the chromatograms from solutions (1) and (4) and calculate the content of sulfadoxine (C12H14N4O4S) and pyrimethamine (C12H13ClN4) in the tablets.
B. Use the average of 10 individual results obtained for each of sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine in the test for uniformity of content.
Uniformity of content
The tablets comply with the test for 5.1 Uniformity of content for single-dose preparations, using the following method of analysis.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the chromatographic conditions as described under Assay, Method A.
For solution (1) transfer one powdered tablet to a 200 mL volumetric flask. Add about 70 mL of acetonitrile R and sonicate for 10 minutes. Allow to cool to room temperature, make up to volume using the mobile phase and sonicate for 10 minutes. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 25 mL with the mobile phase and filter a portion of this solution through a 0.45 μm filter, discarding the first few mL of the filtered solution. For solution (2) transfer 25 mg of sulfadoxine RS, accurately weighed, to about 10 mL of acetonitrile R, sonicate until dissolved and dilute to 25.0 mL with the mobile phase. For solution (3) transfer 25 mg of pyrimethamine RS, accurately weighed, to about 35 mL of acetonitrile R, sonicate until dissolved and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. For solution (4) dilute 10.0 mL of solution (2) and 2.0 mL of solution (3) to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Operate with a flow rate of 2 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 227 nm.
Inject 20 µl of solution (4). The assay is not valid unless the resolution between the peaks due to sulfadoxine and to pyrimethamine, eluting in this order, is at least 5. The run time for the analyses is not less than 25 minutes.
Inject separately 20 µl each of solution (1) and (4).
Measure the areas of the peak responses obtained in the chromatograms for solutions (1) and (4) and calculate the content of sulfadoxine (C12H14N4O4S) and pyrimethamine (C12H13ClN4) in each tablet.
Impurities
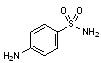
A. 4-aminobenzenesulfonamide (sulfanilamide),
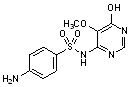
B. 4-amino-N-(6-hydroxy-5-methoxypyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide,
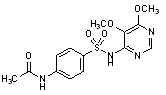
C.N-{4-[(5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-yl)sulfamonyl]phenyl}acetamide,
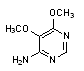
D. 5,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-4-amine.