Reagents, test solutions and volumetric solutions: D - Dantron R.... Dragendorff reagent, modified, TS
Dantron R
1,8-dihydroxyanthraquinone; C14H8O4.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Description. An orange, microcrystalline powder.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Melting point. About 193 °C.
Decaethylene glycol monodocecyl ether R.
Polyoxyethylene 10 lauryl ether; C32H66O11.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Demeclocycline hydrochloride R
Demeclocycline hydrochloride of a suitable quality should be used.
1,4-Di[2-(4-methyl-5-phenyloxazole)]benzene R
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride R
C12H14N4,4HCl,2H2O.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Description. An almost white or slightly pink powder.
Dimethyl-POPOP C26H20N2O2. Suitable for scintillation counting.
3,3'-Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (5g/L) TS
A solution of 3,3'-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride R containing 5 g of C12H14N4,4HCl per litre.
Diammonium hydrogen phosphate (100 g/L) TS
A solution of diammonium hydrogen phosphate R containing about 100 g of (NH4)2HPO4 per litre.
Diammonium hydrogen phosphate R
[ammonium phosphate R]. (NH4)2HPO4 (SRIP, 1963, p.38).
Diatomaceous support R.
Description. White granules of silica consisting chiefly of the skeletons of diatoms. The material is flux-calcined to sequester coloured metallic oxides in a colourless form and is supplied commercially in various forms, such as: acid-washed, silanized and alkali-washed.
Diazepam R
Diazepam of a suitable quality should be used.
Diazobenzenesulfonic acid TS
Procedure. To 0.9 g of sulfanilic acid R add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid (~250 g/L) TS and sufficient water to produce 100 mL. To 3 mL of this solution add 5 mL of sodium nitrite (3 g/L) TS, cool in ice for 5 minutes, add a further 20 mL of sodium nitrite (3 g/L) TS and again cool in ice; dilute with water to 100 mL, keeping the solution cold.
Note: Diazobenzenesulfonic acid TS must be freshly prepared and should not be used until at least 15 minutes after its preparation.
Diazomethane TS
Caution. Diazomethane is explosive in the gaseous state and its explosive decomposition is easily initiated by rough surfaces. Do not use apparatus with ground-glass joints or boiling stones of any kind. Diazomethane is highly toxic and all operations should be conducted under a well-ventilated hood.
Procedure. Prepare a solution of 0.4 g of potassium hydroxide R in 10 mL of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and add it to a solution of 2.14 g of N-methyl-N -nitrosotoluene-4-sulfonamide R in 30 mL of ether R while cooling in ice. If a precipitate forms add just sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to dissolve it. After 5 minutes gently distil the ethereal diazomethane solution from a water-bath. Diazomethane TS contains about 10 g of CH2N2 per litre.
Alternative procedures. Other procedures for the evolution of diazomethane, using other starting materials, may also be employed, provided the resulting solution has the required concentration of CH2N2.
Dibromomethane R
Methylene bromide, CH2Br2.
Description. Colourless to yellowish liquid.
Miscibility. Miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS, ether R and acetone R.
Dibutyl ether R
Di-n-butyl ether, C8H18O.
Caution. Dibutyl ether R tends to form explosive peroxides especially when anhydrous.
Description. A colourless liquid.
Miscibility. Practically immiscible with water; miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Boiling range. 140–143 °C.
Mass density. ρ20 = 0.769 kg/L.
Refractive index. 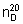 = 1.344.
= 1.344.
Dibutyl phthalate R
Di-n-butyl phthalate, C16H22O4.
Description. A clear, colourless or faintly coloured liquid.
Miscibility. Very slightly miscible with water; miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Mass density. ρ20 = 1.043-1.048 kg/L.
Refractive index. 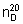 = 1.492–1.495.
= 1.492–1.495.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 0.2 mg/mL.
Dichloroethane R
1,2-Dichloroethane, C2H4Cl2 (SRIP, 1963, p. 76).
Dichlorofluorescein R
C20H10Cl2O5.
Description. A light orange-coloured, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Dichlorofluorescein TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.2 g of dichlorofluorescein R in 100 mL of methanol R.
Dichloromethane R
Methylene chloride, CH2Cl2.
Description. A clear colourless, mobile liquid.
Miscibility. Freely miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Boiling range. Not less than 95% distils between 39 and 41 °C.
Residue on evaporation. Leaves, after evaporation on a water-bath and drying at 105 °C, not more than 0.5 mg/mL.
2,6-Dichloroquinone chlorimide R
C6H2Cl3NO (SRIP, 1963, p. 77).
2,6-Dichloroquinone chlorimide/ethanol TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.5 g of 2,6-dichloroquinone chlorimide R in sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to produce 100 mL.
Dichromate colour TS
A solution containing 4.904 g/L of K2Cr2O7.
Procedure. Prepare a solution containing 490.35 mg of K2Cr2O7 in 100 mL by diluting the strong dichromate colour TS with sulfuric acid (~10 g/L) TS as necessary.
Dichromate colour, strong, TS
Procedure. Dissolve 6.0 g of potassium dichromate R in 120 mL of sulfuric acid (~10 g/L) TS, filter the solution if necessary and determine the concentration of K2Cr2O7.
Assay. Dilute 5.0 mL with sufficient water to produce 50 mL. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a glass-stoppered flask, add 10 mL of water, 2 g of potassium bicarbonate R and 20 mL of sulfuric acid (~100 g/L) TS. Loosely close the flask with its stopper. When the gas evolution has ceased add 1 g of potassium iodide R, keep the flask for 5 minutes in a dark place and titrate the liberated iodine with sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/L) VS using starch TS as indicator. Each mL of sodium thiosulfate (0.1 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 4.904 mg of K2Cr2O7.
Diethoxytetrahydrofuran R
C8H16O3. Mixture of the cis and trans isomers.
Description. Colourless or slightly yellow, clear liquid.
Miscibility. Practically immiscible with water; miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Mass density. ρ20 = about 0.975 kg/L.
Refractive index. 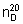 = 1.418.
= 1.418.
Diethoxytetrahydrofuran/acetic acid TS
Procedure. Mix 1 mL of diethoxytetrahydrofuran R with sufficient glacial acetic acid R to produce 100 mL.
Diethyl phthalate R
C12H14O4.
Mass density. ρ20 = about 1.117 kg/L.
Refractive index. 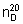 = 1.500–1.505.
= 1.500–1.505.
Diethylamine R
C4H11N. Contains not less than 99.5% of C4H11N.
Description. A clear, colourless liquid.
Mass density. ρ20 = 0.702-0.704 kg/L.
Refractive index. 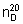 = 1. –1.386.
= 1. –1.386.
Assay. Add about 3 g, accurately weighed, to 50 mL of sulfuric acid (0.5 mol/L) VS and titrate the excess acid with sodium hydroxide (1 mol/L) VS, using methyl red/ethanol TS as indicator. Each mL of sulfuric acid (0.5 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 73.14 mg of C4H11N.
Diethylaminoethylcellulose R
A suitable grade for column chromatography.
Diethylene glycol R
2,2′-Oxydiethanol; C4H10O3 ; CAS Reg. No. 111-46-6.
Contains not less than 99.5% of C4H10O3.
Description. Clear, colourless liquid, hygroscopic, miscible with water R, acetone R and dehydrated ethanol R.
Relative density. 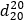 about 1.118.
about 1.118.
Refraction index. 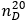 about 1.447.
about 1.447.
Boiling point. 244 °C to 246 °C.
Storage. In an airtight container.
Diethylene glycol succinate R
A suitable grade to be used in gas-liquid chromatography.
Diethylphenylenediamine sulfate TS
Procedure. To 250 mL of water add about 2 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and 50 mL of disodium edetate (0.01 mol/L) VS. Dissolve 1.1 g of N,N -diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate R into this solution and dilute with sufficient water to produce 1000 mL.
N,N-Diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate R
N ,N-Diethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine sulfate; C10H16N2,H2SO4.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Description. A white or slightly coloured powder.
Melting point. About 185 °C with decomposition.
Storage. N,N-Diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate R should be kept protected from light.
2,7-Dihydroxynaphthalene R
C10H8O2. Naphthalene-2,7-diol. CAS Reg. No. 582-17-2
Description. Needles.
Solubility. Soluble in water and in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Melting point. About 190 °C.
2,7-Dihydroxynaphthalene TS
Dissolve 10 mg of 2,7-dihydroxynaphthalene R in 100 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and allow to stand until decolorised.
Storage. Use within 2 days.
Digitonin R
C55H90O29 (SRIP, 1963, p. 78).
Digitonin TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.10 g of digitonin R in sufficient ethanol (~710 g/L) TS to produce 10 mL.
Note: Digitonin TS must be freshly prepared.
Diisopropyl ether R
Isopropyl ether; C6H14O.
Description. A colourless liquid; odour, characteristic.
Boiling point. About 68 °C.
Note. Diisopropyl ether is highly flammable.
Dimethyl sulfoxide R
C2H6OS.
Description. A colourless liquid; odourless or with a slight but unpleasant odour.
Mass density. ρ20 = 1.10 kg/L.
Dimethylacetamide R
C4H9NO.
Description. A colourless liquid.
Boiling temperature. About 165 °C.
Mass density. ρ20 = 0.94 kg/L.
Dimethylamine R
C2H7N.
Description. A low-boiling liquid, 7 °C; odour, characteristic.
Solubility. Soluble in water, ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Dimethylamine/ethanol TS
A solution of dimethylamine R in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS containing about 330 g/L of C2H7N.
Assay. Dilute 2 mL to 10 mL with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS. Transfer 2 mL to a flask containing 50.0 mL of sulfuric acid (0.05 mol/L) VS and mix. Titrate the excess acid with sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS using methyl red/ethanol TS as indicator. Each mL of sulfuric acid (0.05 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 4.508 mg of C2H7N.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R
[dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R]. C9H11NO (SRIP, 1963, p.78).
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS1
Procedure. Dissolve 0.125 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in a cooled mixture of 65 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and 35 mL of water and add 0.2 mL of ferric chloride (25 g/L) TS.
Note: 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS1 must be freshly prepared.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS2
Procedure. Dissolve 0.80 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in a cooled mixture of 80 g of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and 20 g of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS3
Procedure. Dissolve 0.5 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in 50 mL of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS, add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/L) TS and dilute with sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to produce 100 mL.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS4
Procedure. Dissolve 2 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in a mixture of 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/L) TS and 95 mL of glacial acetic acid R.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS5
Procedure. Dissolve without heating 2 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in a mixture of 45 mL of water and 55 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/L) TS.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS6
Procedure. Dissolve 0.2 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in 20 mL of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and add 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/L) TS. Shake the solution with charcoal R and filter. The colour of this test solution is less intense than that of iodine (0.0001 mol/L) VS.
Note: 4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS6 must be freshly prepared.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde TS7
Procedure. Dissolve 0.1 g of 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde R in 1 mL of hydrochloric acid (~420 g/L) TS, dilute with ethanol (~750 g/L) to produce 100 mL.
4-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde R
C11H13NO.
Description. Orange crystals, or a crystalline powder; odour, characteristic.
Solubility. Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS; sparingly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
4-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde TS1
Procedure. Dissolve 2 g of 4-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde R in a mixture of 100 mL of hydrochloric acid (5 mol/L) VS and 100 mL of ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Storage. Store the solution at a temperature of about 0 °C.
4-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde TS2
Procedure. Dilute 20 mL of 4-dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde TS1 with sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to produce 100 mL.
Note: 4-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde TS2 must be freshly prepared.
N,N-Dimethylaniline R
C8H11N.
Description. A colourless liquid darkening on storage.
Miscibility. Practically immiscible with water, miscible with ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Boiling point. About 193 °C.
Mass density. ρ20 = 0.96 kg/L.
Dimethylformamide R
C3H7NO.
Description. A clear and colourless liquid, having a characteristic odour.
Miscibility. Miscible with water and ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Boiling range. Not less than 25% distils at between 152 and 156 °C.
Mass density (ρ20). 0.945–0.947 kg/L.
Acidity and alkalinity. Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of water, add 2 drops of phenolphthalein/ethanol TS; not more than 0.2 mL of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide (0.01 mol/L) VS is required to produce a red colour. Add 0.3 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.01 mol/L) VS and 5 drops of methyl, red/ethanol TS; an orange colour is produced.
N,N-Dimethyloctylamine R
Octyldimethylamine; C10H23N.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Description. A colourless liquid.
Boiling point. About 195 °C.
Dimidium bromide R
C20H18BrN3. 3,8-Diamino-5-methyl-6-phenylphenanthridinium bromide. CAS Reg. No. 518-67-2.
Description. Dark-red crystals.
Solubility. Slightly soluble in water at 20 °C, sparingly soluble in water at 60 °C and in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Storage. Store protected from light.
Dimidium bromide/sulfan blue TS
Procedure. Dissolve separately 0.5 g of dimidium bromide R and 0.25 g of sulfan blue R in 30 mL of a hot mixture of 1 volume of anhydrous ethanol R and 9 volumes of water R, stir, mix the two solutions, and dilute to 250 mL with the same mixture of solvents. Mix 20 mL of this solution with 20 mL of a 14.0 per cent V/V solution of sulfuric acid R previously diluted with about 250 mL of water R and dilute to 500 mL with water R.
Storage. Store protected from light.
Dinitrobenzene R
C6H4N2O4 (SRIP, 1963, p. 79).
Dinitrobenzene/ethanol TS
Procedure. Dissolve 1 g of dinitrobenzene R in sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to produce 100 mL.
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene R
C6H4ClN2O4 (SRIP, 1963, p. 80).
Dinitrogen oxide R
N2O.
A commercially available gas of suitable grade.
Dinonyl phthalate R
C26H42O4.
Description. A colourless to pale yellow, viscous liquid.
Mass density. ρ20 = 0.97–0.98 kg/L.
Refractive index. 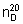 = 1.482–1.489
= 1.482–1.489
Water. Determine as described under 2.8 Determination of water by the Karl Fischer method using about 2 mL of the liquid; not more than 1.0 mg/mL.
Acidity. Shake 5.0 g with 25 mL of water for 1 minute. Allow to stand, filter the aqueous layer and add to it 5 drops of phenolphthalein/ethanol TS; not more than 0.3 mL of carbonate-free sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS is required for the neutralization (0.5 mg/g expressed as phthalic acid).
Dioxan R
1,4-Dioxane, C4H8O2.
Caution. It is dangerous to determine the boiling range or the residue on evaporation before complying with the test for peroxides.
Description. A clear, colourless liquid.
Miscibility. Miscible with water, ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and ether R.
Boiling range. Not less than 95% distils at between 101 and 105 °C.
Melting temperature. Solidifies when cooled in ice and does not completely remelt at temperatures below 10 °C.
Residue on evaporation. Evaporate on a water-bath and dry to constant weight at 105 °C; it leaves a residue of not more than 0.1 mg/mL.
Mass density (ρ20). About 1.031 kg/L.
Water. Determined by the Karl Fischer method, not more than 5.0 mg/mL.
Peroxide. Add 5 mL to a mixture of 1 g of potassium iodide R dissolved in 10 mL of water, 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS, 2 mL of starch TS and mix; not more than a faint blue or brown colour is produced.
Diphenyl ether R
Phenyl ether, C12H10O.
Description. A colourless liquid.
Miscibility. Immiscible with water; freely miscible with glacial acetic acid R and with most organic solvents.
Boiling temperature. About 259 °C.
Melting range. 26–28 °C.
Diphenylamine R
C12H11N (SRIP, 1963, p. 81).
Diphenylamine/sulfuric acid TS
Procedure. Dissolve 1.0 g of diphenylamine R in 100 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS.
Storage. Diphenylamine/sulfuric acid TS must be colourless and should be kept protected from light.
Diphenylbenzidine R
C24H20N2.
Description. A white, or faintly grey-coloured, crystalline powder.
Solubility. Insoluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS and acetone R.
Melting range. 246–250 °C.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Nitrates. Dissolve 8 mg in a cooled mixture of nitrogen-free sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and 5 mL of water; the solution is colourless or not more than very pale blue.
1,5-Diphenylcarbazide R
C13H14N4O.
Description. A white, crystalline powder, gradually turning pink on exposure to air.
Melting point. About 174 °C.
Diphenylcarbazide TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.2 g of 1,5-diphenylcarbazide R in a mixture of 10 mL of glacial acetic acid R and 90 mL of ethanol (~710 g/L) TS.
Sensitivity test to chromate. Dilute 0.5 mL of potassium dichromate (0.0167 mol/L) VS with water to 1000 mL. Dilute 5 mL of this solution to 50 mL with water, add 0.2 mL of hydrochloric acid (2 mol/L) VS and 0.5 mL of diphenylcarbazide TS; a reddish violet colour is produced.
Diphenylcarbazone R
C13H12N4O (SRIP, 1963, p. 81).
Diphenylcarbazone/ethanol TS
A solution of diphenylcarbazone R dissolved in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS containing about 1 g/L of C13H12N4O.
2,5-Diphenyloxazole R
PPO, C15H11NO. Suitable for scintillation counting.
Dipotassium hydrogen phosphate R
K2HPO4 (SRIP, 1963, p. 81).
2,2'-Dipyridyl R
2,2’-Bipyridyl. C10H8N2. Contains not less than 99% of C10H8N2.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Disodium chromotropate (10 g/L) TS
A solution of disodium chromotropate R containing about 9.5 g of C10H6Na2O8S2 per litre.
Disodium chromotropate R
[chromotropic acid sodium salt R]. C10H6Na2O8S2,2H2O.
Description. A yellow to light-brown powder.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Identification. To 0.5 mL of a 2 mg/mL solution add 10 mL of water and 1 drop of ferric chloride (25 g/L) TS; a green colour is produced.
Sensitivity. Dissolve 5 mg in 10 mL of a mixture of 9 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and 4 mL of water. Separately dilute 0.5 mL of formaldehyde TS with water to make 1000 mL. Transfer to each of two separate test-tubes 5 mL of the disodium chromotropate solution, to one add 0.2 mL of the formaldehyde solution and heat both tubes in a water-bath for 30 minutes; a violet colour is produced in the tube containing the formaldehyde solution.
Disodium chromotropate TS
Procedure. Dissolve 5 mg of disodium chromotropate R in 10 mL of a mixture of 9 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and 4 mL of water.
Disodium edetate (0.01 mol/L) VS
Disodium edetate R, dissolved in water to contain 3.342 g of C10H14N2Na2O8 in 1000 mL.
Method of standardization. Ascertain the exact concentration of the solution following an appropriate method, e.g. as described under disodium edetate (0.05 mol/L) VS.
Disodium edetate (0.05 mol/L) VS
Disodium edetate R, dissolved in water to contain 16.71 g of C10H14N2Na2O8 in 1000 mL.
Method of standardization. Ascertain the exact concentration by an appropriate method. The following method is suitable: Transfer about 200 mg of calcium carbonate R2, accurately weighed, to a 400 mL beaker, add 10 mL of water and swirl to form a slurry. Cover the beaker with a watch glass and introduce 2 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS from a pipette inserted between the lip of the beaker and the edge of the watch glass. Swirl the contents of the beaker to dissolve the calcium carbonate. Wash down the sides of the beaker, the outer surface of the pipette and the watch glass with water and dilute with water to about 100 mL. While stirring the solution, preferably with a magnetic stirrer, add about 30 mL of the disodium edetate solution from a 50 mL burette. Add 10 mL of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/L) TS and 0.3 g of calcon indicator mixture R or of calcon carboxylic acid indicator mixture R and continue the titration with the disodium edetate solution to a blue end-point. Each 5.005 mg of calcium carbonate is equivalent to 1 mL of disodium edetate (0.05 mol/L) VS.
Disodium edetate (0.1 mol/L) VS
Disodium edetate R, dissolved in water to contain 33.42 g of C10H14N2Na2O8 in 1000 mL.
Method of standardization. Ascertain the exact concentration of the solution following an appropriate method, e.g. as described under disodium edetate (0.05 mol/L) VS.
Disodium edetate (10 g/L) TS
A solution of disodium edetate R containing about 10 g of disodium edetate R per litre.
Disodium edetate (20 g/L) TS
A solution of disodium edetate R containing about 20 g of disodium edetate R per litre.
Disodium edetate R
C10H14N2Na2O8,2H2O (SRIP, 1963, p. 82).
Disodium hydrogen phosphate (100 g/L) TS
A solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R containing about 100 g of Na2HPO4 per litre.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate (28.4 g/L) TS
A solution of anhydrous disodium hydrogen phosphate R containing 28.4 g of Na2HPO4 per litre.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate (40 g/L) TS
A solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R containing about 40 g of Na2HPO4 per litre.
Disodium hydrogen phosphate R
[sodium phosphate R]. Na2HPO4,12H2O (SRIP, 1963, p.192).
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous, R
[sodium phosphate, anhydrous, R]. Na2HPO4 (SRIP, 1963, p. 193).
5,5'-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) R
3-Carboxy-4-nitrophenyl disulfide; C14H8N2O8S2.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
5,5'-Dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid/methanol TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.198 g of 5,5'-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid) R in sufficient methanol R to produce 500 mL.
Storage. Keep under refrigeration, and warm to room temperature before use.
Dithiol R
C7H8S2 CAS[496-74-2]
Toluene-3, 4-dithiol. 4-methylbenzene-1,2-dithiol.
Hygroscopic white crystals soluble in methanol and in alkali hydroxides solutions.
Dithiol reagent R
Prepare immediately before use. Dissolve 1 g of dithiol R by adding 2 mL thioglycollic acid R and dilute to 250 mL with 20 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R.
Dithizone R
C13H12N4S (SRIP, 1963, p. 83).
Dithizone standard TS
Procedure. Dissolve 10 mg of dithizone R in 1000 mL of chloroform R.
Storage. Store the solution in a glass-stoppered, lead-free bottle, protected from light and kept at a temperature not exceeding 4 °C.
Dithizone TS
Procedure. Dissolve 0.10 g of dithizone R in sufficient ethanol (~750 g/L) TS to produce 100 mL.
Docusate sodium R
Sodium 1,4-bis[(2-ethylhexyl)oxy]-1,4-dioxobutane-2-sulfonate.
A commercially available reagent of suitable grade.
Domiphen bromide (10 g/L) TS
A solution of domiphen bromide R containing about 10 g of C22H40BrNO per litre.
Domiphen bromide R
Dodecyldimethyl(2-phenoxyethyl)ammonium bromide; C22H40BrNO.
Description. Colourless or faintly yellow, crystalline flakes.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water and ethanol (~750 g/L) TS; soluble in acetone R.
Dopamine hydrochloride RS.
International Chemical Reference Substance.
Dragendorff reagent TS
Procedure. Shake vigorously to dissolve 0.85 g of bismuth subnitrate R in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid R and 40 mL of water (solution A). Dissolve 8 g of potassium iodide R in 20 mL of water (solution B). Immediately before use mix together equal volumes of solutions A and B and glacial acetic acid R.
Storage. Solutions A and B must be protected from light.
Dragendorff reagent, modified, TS
Procedure. Add 20 mL of acetic acid (~60 g/L) TS to 4 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of solutions A and B of Dragendorff reagent TS.
Note: Prepare this solution immediately before use.