Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Ephedrine sulfate (Ephedrini sulfas)
Molecular formula. (C10H15NO)2,H2SO4
Relative molecular mass. 428.5
Graphic formula.
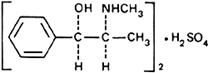
Chemical name. (-)-Ephedrine sulfate (2:1) (salt); [R-(R*,S*)]-α-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]benzenemethanol sulfate (2:1) (salt); CAS Reg. No. 134-72-5.
Description. Colourless crystals or a white, crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Antiasthmatic drug.
Storage. Ephedrine sulfate should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Ephedrine sulfate darkens on exposure to light. Even in the absence of light, it is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Ephedrine sulfate contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 101.0% of (C10H15NO)2,H2SO4, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
A. The absorption spectrum of a 1.0 mg/mL solution, when observed between 230 nm and 350 nm, exhibits maxima at about 251 nm, 257 nm, and 262 nm; the absorbances of a 1-cm layer at these wavelengths are about 0.61, 0.76, and 0.61, respectively.
B. Dissolve 10 mg in 1 mL of water and add 0.1 mL of copper(II) sulfate (80 g/l) TS, followed by 2 mL of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS; a violet colour is produced. Add 1 mL of ether R and shake; a purple colour is produced in the ethereal layer and a blue colour in the aqueous layer.
C. Dissolve 0.05 g in 5 mL of water. Add a few drops of sodium hydroxide (~80 g/l) TS and 4 mL of potassium ferricyanide (50 g/l) TS, and heat; an odour of benzaldehyde is perceptible.
D. A 20 mg/mL solution yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of sulfates.
E. Melting temperature, about 245 °C with decomposition.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 50 mg/mL solution and calculate with reference to the dried substance; 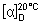 = -30.5° to -32.5°.
= -30.5° to -32.5°.
Chlorides. A quantity of 0.20 g of the test substance shows no more turbidity than 0.40 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.02 mol/l) VS when subjected to the procedure described under 2.2.1 Limit test for chlorides; the chloride content is not more than 1.4 mg/g.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 1.0 g in 10 mL of water is clear, or not more opalescent than opalescence standard TS2, and colourless.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 20 mg/g.
Acidity and alkalinity. Dissolve 1.0 g in 10 mL of water and add 0.1 mL of methyl red/ethanol TS; not more than 0.1 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS or 0.1 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS is required to obtain the midpoint of the indicator (orange).
Assay. Dissolve about 0.3 g, accurately weighed, in 10 mL of water, add about 3 g of sodium chloride R to saturate the solution, then add 5 mL of sodium hydroxide (1 mol/l) VS and extract with 4 volumes, each of 25 mL, of chloroform R. Wash the combined chloroform extracts with 10 mL of a saturated solution of sodium chloride R, and filter through purified cotton saturated with chloroform R. Shake the aqueous wash solution with 10 mL of chloroform R and add it to the main chloroform extract. Add 0.25 mL of methyl red/ethanol TS and titrate with perchloric acid/dioxan (0.1 mol/l) VS, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method A. Each mL of perchloric acid/dioxan (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 21.43 mg of (C10H15NO)2,H2SO4.