Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Ketamine hydrochloride (Ketamini hydrochloridum)
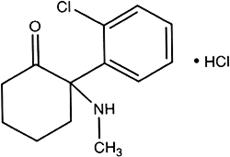
C13H16ClNO,HCl
Relative molecular mass. 274.2
Chemical name. (±)-2-(o-Chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone hydrochloride; (±)-2-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methylamino)cyclohexanone hydrochloride; CAS Reg. No. 1867-66-9.
Description. A white, crystalline powder; odour, characteristic.
Solubility. Freely soluble in water and methanol R; soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. General anaesthetic.
Storage. Ketamine hydrochloride should be kept in a well-closed container.
Requirements
Ketamine hydrochloride contains not less than 98.5% and not more than the equivalent of 101.0% of C13H16ClNO,HCl, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and D or tests B, C, and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from ketamine hydrochloride RS or with the reference spectrum of ketamine hydrochloride.
B. The absorption spectrum of a 0.33 mg/mL solution in hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS, when observed between 230 nm and 350 nm, exhibits 2 maxima at about 269 nm and 276 nm. The ratio of the absorbance at 269 nm to that at 276 nm is between 1.10 and 1.22.
C. Dissolve 1 g in 10 mL of water and add 1 mL of sulfuric acid (~100 g/l) TS and 1 mL of ammonium reineckate (10 g/l) TS; a light red precipitate is produced.
D. A 0.1 g/mL solution yields reaction B described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of chlorides.
Melting range. 258-261 °C.
Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 1; determine the heavy metals content according to Method A; not more than 20 μg/g.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 2 g in 10 mL of water is clear and colourless.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant mass at 105 °C; it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
pH value. pH of a 0.1 g/mL solution, 3.5-4.1.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R1 as the coating substance and a mixture of 49 volumes of cyclohexane R and 1 volume of isopropylamine R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 2 μl of each of two solutions in methanol R containing (A) 50 mg of Ketamine hydrochloride per mL and (B) 0.25 mg of Ketamine hydrochloride per mL. Develop the plate for a distance of 10 cm. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and spray the plate evenly with modified Dragendorff reagent TS, dry, spray with hydrogen peroxide (~60 g/l) TS, and examine the chromatogram in daylight.
Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. Dissolve 0.200 g in 50 mL of methanol R and add 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS. Carry out a potentiometric titration, using sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration. Read the volume added between the two points of inflexion.
1 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 27.42 mg of C13H16ClNO,HCl.
Additional requirements for Ketamine hydrochloride for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 0.4 IU of endotoxin RS per mg.