Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Methylthioninium chloride (Methylthioninii chloridum)
Molecular formula. C16H18ClN3S, x H2O.
Relative molecular mass. 319.9 (anhydrous).
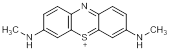
Graphic formula
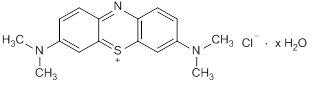
Chemical name. C.I. Basic Blue 9; 3,7-bis(dimethylamino)-5λ4-phenothiazin-5-ylium chloride hydrate; CAS Reg. No. 122965-43-9.
Other name. Methylene blue.
Description. Dark blue or dark green crystalline powder with a metallic sheen.
Solubility. Slightly soluble in water R and in ethanol (~750 g/L) TS.
Category. Antidote.
Storage. Methylthioninium chloride should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Requirements
Definition. Methylthioninium chloride contains not less than not less than 93.0% and not more than 102.0% of C16H18ClN3S, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
- Either tests A and F or any two of tests B, C, D or E together with test F may be applied.
A. Dry a small quantity of the test substance for 5 hours at 105 °C and carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from methylthioninium chloride RS, which has also been dried under the conditions mentioned above for the test substance, or with the reference spectrum of methylthioninium chloride.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.4 High-performance-liquid chromatography using the conditions given under “Assay”. The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to methylthioninium in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. The absorption spectrum (1.6) of a 5 μg per mL solution in hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS, when observed between 230 nm and 800 nm, exhibits 4 maxima at about 255–260 nm, 285–290 nm, 670–680 nm, and 740–750 nm.
D. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 3 volumes of acetic acid R, 3 volumes of ethanol R and 4 volumes of water R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 2 µL of each of the following 2 solutions in methanol R containing (A) 0.1 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.1 mg of methylthioninium chloride RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in air or in a current of cool air. Examine the chromatogram in daylight.
The principal spot obtained with solution (A) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity to that obtained with solution (B).
E. Dissolve 1 mg of the test substance in 10 mL of water R; a deep blue colour is produced. Add 2.0 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/L) TS and 0.25 g of zinc R powder; the colour of the solution is discharged. Filter and expose the filtrate to the air; the blue colour of the solution reappears.
F. Mix 0.05 g of test substance with 0.5 g of anhydrous sodium carbonate R in a porcelain crucible. Carefully heat the mixture to a red glow for 10 minutes. Cool, dissolve the residue in 10 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/L) TS and filter. The filtrate yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of chlorides.
Copper. Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) ignite 1.0 g in a porcelain crucible using as low a temperature as practicable, until all of the carbon is oxidized. Cool the residue, add 15 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/L) TS and boil for 5 minutes. For solution (2) boil a quantity of copper(II) sulfate R, equivalent to 300 μg of Cu, with 15 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/L) TS for 5 minutes. Filter separately the cooled solutions (1) and (2) and wash any residue with 10 mL of water R. Combine the filtrate and washings of the solution (1) and similarly combine the filtrate and washings of the solution (2); add to each an excess of ammonia (~100 g/L) TS and filter the solutions into 50 mL volumetric flasks. Wash the precipitates with small portions of water R, adding the washings to the filtrates; dilute the contents of each flask with water R to volume, mixing thoroughly. To 25 mL of each of the solutions add 10 mL of hydrogen sulfide TS; any dark colour produced in solution (1) is not more intense than that of solution (2) (the copper content is not more than 0.30 mg/g).
Iron. Mix 4 g with 200 mL of water R in a long-necked, round-bottomed flask, add 15 mL of nitric acid (~1000 g/L) TS, heat carefully to boiling and continue boiling until the volume of liquid is reduced to about 20 mL. Allow to cool, add 10 mL of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/L) TS and mix. Heat to boiling and add small successive quantities of nitric acid (~1000 g/L) TS, cooling before each addition, until a colourless liquid is obtained. Heat until white fumes are evolved; if darkening occurs at this stage continue the treatment with nitric acid (~1000 g/L) TS. Finally heat until white fumes are again evolved. Allow the colourless liquid to cool, add 25 mL of a saturated solution of ammonium oxalate R in water R, and boil until the slight froth completely subsides. Cool, dilute to 50 mL with water R; 5 mL of the diluted solution complies with the 2.2.4 Limit test for iron; not more than 0.20 mg/g.
Sulfated ash (2.3). Not more than 2.5 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry at 105 °C for 5 hours; it loses not more than 240 mg/g.
Related substances
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using the chromatographic conditions as described under "Assay".
Prepare the following solutions using as the diluent a mixture of 70 volumes of a 0.1% (v/v) solution of trifluoroacetic acid R (mobile phase A) and 30 volumes of acetonitrile R (mobile phase B). For solution (1) dissolve about 50 mg of the test substance and dilute to 50.0 mL. Sonicate for 5 minutes. For solution (2) dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3) dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 50.0 mL. For solution (4) dissolve 10 mg of methylthioninium chloride RS (containing methylthioninium chloride and impurity A) and dilute to 10.0 mL.
Inject alternately 5 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (3), (4).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) and the chromatogram supplied with methylthioninium chloride RS to identify the peak due to impurity A. Impurity A is eluted at the relative retention of about 0.8 with reference to methylthioninium (retention time about 11 minutes). The test is not valid unless the resolution between the peaks corresponding to methylthioninium and impurity A is at least 3.5.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
- the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A is not greater than 5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (2) (5.0%);
- the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (3) (0.10%);
- the sum of the areas of all impurity peaks, other than the peak corresponding to impurity A, is not greater than 5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (3) (0.5%). Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.5 times the area of the principal peak obtained with solution (3) (0.05%).
Assay
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography using a stainless steel column (10 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded phenylsilyl groups (3.5 µm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
mobile phase A: 0.1 % (v/v) solution of trifluoroacetic acid R;
mobile phase B: acetonitrile R.
|
Time (minutes) |
Mobile phase A (% v/v) |
Mobile phase B (% v/v) |
Comments |
|
0–5 |
80 |
20 |
Isocratic |
|
5–25 |
80 to 30 |
20 to 70 |
Linear gradient |
|
25–32 |
30 |
70 |
Isocratic |
|
32–35 |
30 to 80 |
70 to 20 |
Return to initial composition |
|
35–40 |
80 |
20 |
Re-equilibration |
Operate with a flow of 1.0 mL/min. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 246 nm. Maintain the column temperature at 30 °C.
Prepare the following solutions using as diluent a mixture of 30 volumes of acetonitrile R and 70 volumes of mobile phase A. For solution (1) dissolve about 50 mg of the test substance, accurately weighed, and dilute to 50.0 mL. Sonicate for 5 minutes. For solution (2) dissolve 50.0 mg of methylthioninium chloride RS and dilute to 50.0 mL. Sonicate for 5 minutes.
Inject alternately 5 µL each of solutions (1) and (2). The test is not valid unless in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) the symmetry factor of the methylthioninium peak is not more than 3.5.
Measure the areas of the peak responses obtained in the chromatograms from solutions (1) and (2) and calculate the percentage content of methylthioninium chloride (C16H18ClN3S) with reference to the dried substances, using the declared content of C16H18ClN3S in methylthioninium chloride RS.
Additional requirements for Methylthioninium chloride for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for Parenteral preparations.
Bacterial endotoxins. If intended for use in the manufacture of a parenteral dosage forms without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins, carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 2.5 IU of endotoxin RS per mg methylthioninium chloride.
Impurities
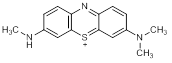
A. 3-(dimethylamino)-7-(methylamino)-5λ4-phenothiazin-5-ylium (azure B cation) (degradation product)
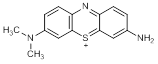
B. 3-amino-7-(dimethylamino)-5λ4-phenothiazin-5-ylium (azure A cation) (degradation product)
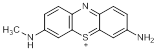
C. 3-amino-7-(methylamino)-5λ4-phenothiazin-5-ylium (azure C cation) (degradation product)
D. 3,7-bis(methylamino)-5λ4-phenothiazin-5-ylium (degradation product)