Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Naloxone hydrochloride (Naloxoni hydrochloridum)
Naloxone hydrochloride, anhydrous
Naloxone hydrochloride, dihydrate
Molecular formula. C19H21NO4,HCl (anhydrous); C19H21NO4,HCl,2H2O (dihydrate).
Relative molecular mass. 363.8 (anhydrous); 399.9 (dihydrate).
Graphic formula.
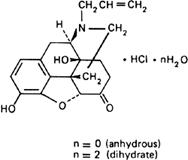
Chemical name. (-)-17-Allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride; 4,5a-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-17-(2-propenyl)morphinan-6-one hydrochloride; (-)-12-allyl-7,7a,8,9-tetrahydro-3,7a-dihydroxy-4aH-8,9c-imino-ethanophenanthro[4,5-bcd]furan-5(6H)-one hydrochloride; CAS Reg. No. 357-08-4 (anhydrous).
(-)-17-Allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride dihydrate; 4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxy-17-(2-propenyl)morphinan-6-one hydrochloride dihydrate; (-)-12-allyl-7,7a,8,9-tetrahydro-3,7a-dihydroxy-4aH-8,9c-imino-ethanophenanthro[4,5-bcd]furan-5(6H)-one hydrochloride dihydrate; CAS Reg. No. 51481-60-8 (dihydrate).
Description. A white or almost white powder.
Solubility. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS; practically insoluble in ether R.
Category. Narcotic antagonist.
Storage. Naloxone hydrochloride should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Naloxone hydrochloride should state whether the substance is in the anhydrous form or is the dihydrate.
Additional information. Even in the absence of light, Naloxone hydrochloride is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures. It melts at about 177°C.
Requirements
Definition. Naloxone hydrochloride contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 102.0% of C19H21NO4,HCl, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either test A or tests B and C may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from naloxone hydrochloride RS or with the reference spectrum of naloxone hydrochloride.
B. Dissolve 0.05 g in 5 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS and add 0.3 mL of ferric chloride (25 g/l) TS; a purplish blue colour is produced.
C. A 0.05 g/mL solution yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of chlorides.
Specific optical rotation. Use a 25 mg/mL solution and calculate with reference to the dried substance; 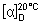 = -170° to -181°.
= -170° to -181°.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; anhydrous Naloxone hydro-chloride loses not more than 5.0 mg/g. Naloxone hydrochloride dihydrate loses not more than 110 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R1 as the coating substance, and as the mobile phase prepare the following solution: shake 100 mL of 1-butanol R with 60 mL of ammonia (~17 g/l) TS, discard the lower layer, and mix 95 volumes of the upper layer with 5 volumes of methanol R. Dry the plate in a current of air. Apply separately to the plate 5μl of each of the two following solutions. For solution (A) dissolve 40 mg of Naloxone hydrochloride in 2 mL of water and dilute to 5 mL with methanol R. For solution (B) dilute 0.5 mL of solution A to 100 mL with methanol R. Develop the chromatogram protected from light. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air, spray with ferric chloride/potassium ferricyanide TS, and examine the chromatogram in daylight.
Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B (0.5%). Disregard any spot remaining at the point of application.
Chlorides content. Dissolve about 0.3 g, accurately weighed, in 50 mL of methanol R. Add 5 mL of glacial acetic acid R and 0.1 mL of eosin Y (5 g/l) TS, and titrate with silver nitrate (0.1 mol/l) VS until a pink colour is produced. Each mL of silver nitrate (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 3.545 mg of Cl; the content of chlorides is not less than 95.4 mg/g and not more than 99.4 mg/g, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Assay. Dissolve 0.300 g in 50 mL of dehydrated ethanol R and add 5.0 mL of hydrochloric acid (0.01 mol/L) VS. Carry out a potentiometric titration using sodium hydroxide/ethanol (0.1 mol/L) VS, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration. Read the volume added between the two points of inflexion.
1 mL of sodium hydroxide/ethanol (0.1 mol/L) VS is equivalent to 36.38 mg of C19H21NO4,HCl.
Additional requirements for Naloxone hydrochloride for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".
Bacterial endotoxins. Carry out the test as described under 3.4 Test for bacterial endotoxins; contains not more than 500 IU of endotoxin RS per mg.