Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Neostigmine metilsulfate (Neostigmini metilsulfas)
Molecular formula. C13H22N2O6S
Relative molecular mass. 334.4
Graphic formula.
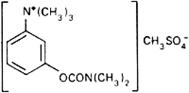
Chemical name. (m-Hydroxyphenyl)trimethylammonium methyl sulfate dimethylcarbamate; 3-[[(dimethylamino)carbonyl]oxy]-N,N,N-trimethylbenzenaminium methyl sulfate; CAS Reg. No. 51-60-5.
Description. A white, crystalline powder; odourless.
Solubility. Very soluble in water; freely soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS.
Category. Cholinergic.
Storage. Neostigmine metilsulfate should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Requirements
Definition. Neostigmine metilsulfate contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 100.5% of C13H22N2O6S, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and D or tests B, C and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from neostigmine metilsulfate RS or with the reference spectrum of neostigmine metilsulfate.
B. See the test described under "Related substances". The spot obtained with solution B corresponds in position, appearance, and intensity with that obtained with solution C.
C. Heat 0.05 g with 0.4 g of potassium hydroxide R and 2 mL of ethanol (~750 g/l) TS on a water-bath for 3 minutes. Adjust to the original volume with ethanol (~750 g/l) TS, cool, and add 2 mL of water and 2 mL of diazobenzenedisulfonic acid TS; a red colour is produced.
D. Mix 20 mg with 0.5 g of sodium carbonate R and heat to fusion in a small crucible; boil the fused mass with 10 mL of water until it has disintegrated, then filter. Add 0.2 mL of bromine TS1 to the filtrate, heat to boiling, acidify with hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS, and expel the excess of bromine by boiling; the resulting solution yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of sulfates.
Melting range. 144-149°C, after drying at 105°C for 3 hours.
Chlorides. Dissolve 0.20 g in 10 mL of water, add 1 mL of nitric acid (~130 g/l) TS and 1 mL of silver nitrate (40 g/l) TS; no immediate appearance of opalescence is observed.
Sulfates. Dissolve 0.20 g in 10 mL of water, add 1.5 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS and 1 mL of barium chloride (50 g/l) TS; no ready appearance of turbidity is produced.
Clarity and colour of solution. A solution of 0.20 g in 10 mL of water is clear and not more intensely coloured than standard colour solution Bnl when compared as described under 1.11.1 Colour of liquids.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 105°C; it loses not more than 10 mg/g.
Acidity. Dissolve 0.20 g in 10 mL of water and add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein/ethanol TS; the test solution is colourless. Add 0.30 mL of sodium hydroxide (0.01 mol/l) VS; the solution turns red.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R1 as the coating substance and a mixture of 67 volumes of water, 30 volumes of methanol R, and 3 volumes of diethylamine R as the mobile phase (a certain type of precoated plate may not be suitable with this mobile phase). Apply separately to the plate 10 μl of each of 3 solutions containing (A) 20 mg of the test substance per mL, (B) 0.10 mg of the test substance per mL, and (C) 0.10 mg of neostigmine metilsulfate RS per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in a current of warm air, spray it with 4-nitroaniline TS2 and then with sodium hydroxide (0.1 mol/l) VS. Dry the plate again in a current of warm air, spray it with potassium iodobismuthate TS2, and examine the chromatogram in daylight. Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. In order to avoid overheating in the reaction medium, mix thoroughly throughout the titration and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.230 g in 2 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and add 50 mL of acetic anhydride R. Carry out a potentiometric titration using perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) VS, as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid (0.1 mol/L) is equivalent to 30.32 mg of C12H19BrN2O2.
Additional requirement for Neostigmine metilsulfate for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".