Monographs: Pharmaceutical substances: Salbutamol sulfate (Salbutamoli sulfas)
Molecular formula. (C13H21NO3)2,H2SO4
Relative molecular mass. 288.4
Graphic formula.
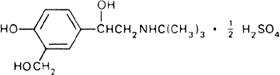
Chemical name. α1-[(tert-Butylamino)methyl]-4-hydroxy-m-xylene-α,α'-diol sulfate (2:1) (salt); α1-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]methyl]-4-hydroxy-1,3-benzenedimethanol sulfate (2:1) (salt); CAS Reg. No. 51022-70-9.
Description. A white or almost white powder; odourless.
Solubility. Soluble in 4 parts of water; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and ether R.
Category. Antiasthmatic drug.
Storage. Salbutamol sulfate should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from light.
Additional information. Even in the absence of light, Salbutamol sulfate is gradually degraded on exposure to a humid atmosphere, the decomposition being faster at higher temperatures.
Requirements
Definition. Salbutamol sulfate contains not less than 98.0% and not more than 101.0% of C13H21NO3,1/2H2SO4, calculated with reference to the dried substance.
Identity tests
• Either tests A and D or tests B, C and D may be applied.
A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from salbutamol sulfate RS or with the reference spectrum of salbutamol sulfate.
B. The absorption spectrum of a 0.080 mg/mL solution in hydrochloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS, when observed between 230 nm and 350 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 276 nm; the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at this wavelength is about 0.46.
C. Dissolve 0.05 g in 5 mL of water and add 0.1 mL of ferric chloride (25 g/l) TS; a reddish violet colour is produced. Add 0.05 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate R; a fleshy precipitate is produced with an evolution of gas. Add a few drops of sulfuric acid (~1760 g/l) TS; the solution becomes colourless.
D. A 20 mg/mL solution yields reaction A described under 2.1 General identification tests as characteristic of sulfates.
Sulfated ash. Not more than 1.0 mg/g.
Loss on drying. Dry to constant weight at 100°C under reduced pressure (not exceeding 0.6 kPa or about 5 mm of mercury); it loses not more than 5.0 mg/g.
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R1 as the coating substance and a mixture of 4 volumes of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, 16 volumes of water, 30 volumes of 2-propanol R, and 50 volumes of ethyl acetate R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of 2 solutions containing (A) 20 mg of the test substance per mL and (B) 0.10 mg of the test substance per mL. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air until the solvents have evaporated. Place the plate for a few minutes in an atmosphere saturated with diethylamine R, spray it with diazotized sulfanilic acid TS, and examine the chromatogram in daylight. Any spot obtained with solution A, other than the principal spot, is not more intense than that obtained with solution B.
Assay. Dissolve about 0.9 g, accurately weighed, in 30 mL of glacial acetic acid R1 and titrate with perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS as described under 2.6 Non-aqueous titration, Method A. Each mL of perchloric acid (0.1 mol/l) VS is equivalent to 57.67 mg of C13H21NO3,1/2H2SO4.
Additional requirement for Salbutamol sulfate for parenteral use
Complies with the monograph for "Parenteral preparations".