Monographs: Dosage forms: Specific monographs: Pyrantel oral suspension (Pyranteli solutio peroralum)
Category. Anthelminthic.
Storage. Pyrantel oral suspension should be kept in a tightly closed container, protected from light.
Labelling. The designation on the container of Pyrantel oral suspension should state that the active ingredient is in the embonate form and the quantity should be indicated in terms of the equivalent amount of pyrantel.
Additional information. Strength in the current WHO Model list of essential medicines: 50 mg of pyrantel/mL.
Requirements
Complies with the monograph for "Liquid preparations for oral use".
Definition. Pyrantel oral suspension is a suspension of pyrantel embonate in a suitable vehicle which may be flavoured. It contains not less than 90.0% and not more than 110.0% of the amount of pyrantel (C11H14N2S) stated on the label.
Identity tests
• Either tests A, or any two of tests B, C, D and E may be applied.
To a quantity of the oral suspension containing the equivalent of about 20 mg of pyrantel add a mixture of 10 mL of dichloromethane R, 10 mL of methanol R and about 1 mL of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, shake and filter. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness on a water-bath, dissolve in a small volume of methanol R (about 3 mL) by heating on a water-bath and then allowing the solution to cool. Separate the crystals, dry at 80 °C for 2 hours and use the dried crystals for "Identity tests A, C and D".
A. Carry out the examination with the dried crystals as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from pyrantel embonate RS or with the reference spectrum of pyrantel embonate.
B. See the test described under Related substances method A. The principal spots obtained with solution (1) correspond in position, appearance and intensity with those obtained with solution (3).
C. The absorption spectrum (1.6) of a 13 μg/mL solution of the dried crystals in methanol R, when observed between 230 nm and 360 nm, exhibits 2 maxima at about 288 nm and 300 nm. The ratio of the maximum absorbance at about 288 nm to that at about 300 nm is about 1.0.
D. Dissolve about 5 mg of the dried crystals in 1 mL of hydrochloric acid (~70 g/l) TS and add 1 mL of formaldehyde/sulphuric acid TS; a violet-red colour is produced.
E. See the test described under Assay. The retention times of the principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained from solution (1) are similar to those obtained from solution (2).
pH value. (1.3) pH of the oral suspension, 4.5–6.0.
Related substances
Carry out the operations in subdued light and without any prolonged interruptions, preferably using low-actinic glassware.
• Either method A or B may be applied.
A. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 3 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 1 volume of water R and 1 volume of glacial acetic acid R as the mobile phase.
To a quantity of the oral suspension equivalent of about 35 mg of pyrantel add a mixture of 10 mL of dichloromethane R, 10 mL of methanol R and about 1 mL of ammonia (~260 g/l) TS, shake and filter. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness on a water-bath and dissolve the dried residue in 10.0 mL dimethylformamide R (1). For solution (2) dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100 mL with dimethylformamide. For solution (3) use 10 mg of pyrantel embonate RS (equivalent to about 3.5 mg of pyrantel) per mL dimethylformamide. For solution (4) expose a quantity of solution (3) under 2000 lx illumination for 24 hours.
Apply separately to the plate 5 μl of each of the solutions (1), (2), (3) and (4).
After application allow the spots to dry for 15 minutes in a current of air. Develop over a path of 12 cm. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber allow it to dry in a current of air for 10 minutes. Examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
Pyrantel and related substances have the following Rf values: impurity A about 0.2; pyrantel about 0.3; embonic acid about 0.9. The test is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) exhibits three well separated spots.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) any spot, other than the two principal spots, is not more intense than the pyrantel spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%). Disregard any spot remaining at the point of application.
B. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions given under Assay.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) transfer a quantity of the oral suspension containing the equivalent of about 25 mg of pyrantel into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Add 7 mL of a mixture composed of 5 volumes of glacial acetic R, 5 volumes of water R and 2 volumes of diethylamine R. Shake and dilute to volume with acetonitrile R, mix and filter. For solution (2) dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100 mL with mobile phase. For solution (3) expose 10 mL of solution (1) under 2000 lx illumination for 24 hours.
Inject separately 20 μl of each of solution (1), (2) and (3) and record the chromatograms for 4 times the retention time of pyrantel.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) the following peaks are eluted at the following relative retention times with reference to pyrantel (retention time about 14 minutes): embonic acid about 0.5; impurity A about 1.3. The test is not valid unless the resolution factor between the pyrantel peak and the impurity A peak is at least 4.0.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) the area of any impurity peak is not greater than the area of the pyrantel peak obtained with solution (2) (1.0%).
Assay
Carry out the operations in subdued light and without any prolonged interruptions, preferably using low-actinic glassware.
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with high-purity base particles of silica gel for chromatography R (5 μm).
As the mobile phase use a mixture of 92.8 volumes of acetonitrile R and 7.2 volumes of a solvent mixture composed of 5 volumes of glacial acetic R, 5 volumes of water R and 2 volumes of diethylamine R.
Prepare the following solutions. For solution (1) transfer a quantity of the oral suspension containing the equivalent of about 7.0 mg of pyrantel, accurately weighed, into a 50 mL volumetric flask. Add about 30 mL of mobile phase, shake for 10 minutes and dilute with mobile phase to volume, mix and filter. Transfer 2.0 mL of the clear filtrate to a 10 mL volumetric flask, dilute with mobile phase to volume and mix. For solution (2) prepare a solution of 0.40 mg of pyrantel embonate RS (equivalent to about 0.14 mg of pyrantel) per mL mobile phase. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a 10 mL volumetric flask, dilute with mobile phase to volume and mix to obtain a standard preparation having a known concentration of 80 μg of pyrantel embonate RS (equivalent to about 28 μg of pyrantel) per mL.
Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of about 288 nm.
Inject separately 20 μl each of solution (1) and (2) and record the chromatograms.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) the peak due to embonic acid is eluted at a relative retention time of about 0.5 with reference to pyrantel (retention time about 14 minutes).
Measure the areas of the peak responses due to pyrantel obtained in the chromatograms from solution (1) and solution (2). Determine the weight per mL (1.3.1) of the oral suspension and calculate the content of pyrantel (C11H14N2S), weight in volume in the oral suspension using the declared content of C11H14N2S,C23H16O6 in pyrantel embonate RS. Each mg of pyrantel embonate C11H14N2S,C23H16O6 is equivalent to 0.3469 mg of pyrantel C11H14N2S.
Impurities
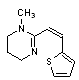
A. 1-methyl-2-[(1E)-2-(thiophen-2-yl)ethenyl]-1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine