Monographs: Dosage forms: Specific monographs: Isoniazid tablets (Isoniazidi compressi)
Category. Antituberculosis medicine.
Storage. Isoniazid tablets should be kept in a well-closed container, protected from moisture and light.
Additional information. Strength in the current WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (EML): tablets: 100 mg to 300 mg; scored tablets: 50 mg.Strength in the current EML for Children: tablets: 100 mg to 300 mg; scored tablets 50 mg.
Requirements
The tablets comply with the monograph on Tablets.
Definition. Isoniazid tablets contain not less than 90.0% and not more than 110.0% of the amount of C6H7N3O stated on the label.
Identity tests
-
Either test A alone or any two of tests B, C or D may be applied.
-
To a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing about 0.1g of Isoniazid, add 10 mL of ethanol (~750g/L) TS and shake for 15 minutes. Centrifuge and decant the supernatant liquid. Extract the remaining liquid with two further 10-mL quantities of ethanol (~750g/L) TS and evaporate the combined extracts to dryness. Carry out the examination with the residue as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from isoniazid RS or with the reference spectrum of isoniazid.
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using the conditions and solutions given under "Assay". The retention time of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the retention time of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, Thin-layer chromatography, using silica gel R6 as the coating substance and a mixture of 5 volumes of ethyl acetate R, 2 volumes of acetone R, 2 volumes of methanol R, and 1 volume of water R as the mobile phase. Apply separately to the plate 10 μL of each of the following solutions. For solution (A), shake a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 0.10 g of Isoniazid with 10 mL of methanol R, filter, and use the filtrate. For solution (B), use a solution containing 10 mg of isoniazid RS per mL of methanol R. After removing the plate from the chromatographic chamber, allow it to dry in air and examine the chromatogram in ultraviolet light (254 nm).
The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (A) corresponds in position, appearance and intensity with the spot due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (B).
-
Carry out as described under 1.6 Spectrophotometry in the visible and ultraviolet regions. Transfer a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 25 mg of Isoniazid, to a 50 mL volumetric flask, add 40 mL of methanol R and sonicate for 5 minutes. Dilute to volume with methanol R and mix. Filter the suspension and dilute 2 mL of the filtrate to 100 mL with methanol R. The absorption spectrum of the test solution, when observed between 200 nm and 400 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 263 nm.
Alternatively, and in combination with identity test B, where a diode-array detector is available, record the UV spectrum of the principal peaks in the chromatograms with a diode array detector in the range of 200 nm to 400 nm. The UV spectrum of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds to the UV spectrum of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
Dissolution. Carry out the test described under 5.5 Dissolution test for oral dosage forms, using as the dissolution medium 900 mL of hydrochloric acid (~0.365 g/L) TS and rotating the paddle at 100 revolutions per minute. At 45 minutes, withdraw a sample of 10 mL of the medium through an in-line filter. Allow the filtered sample to cool to room temperature and dilute a suitable volume of the filtrate with dissolution medium to obtain a solution nominally containing about 0.025 mg of isoniazid per mL (for 50 mg tablets dilute the sample twofold, for 100 mg fourfold and for 300 mg tablets twelvefold).
Measure the absorbance as described under 1.6 Spectrophotometry in the visible and ultraviolet regions of the resulting solution in a cuvette with an optical pathlength of 10 mm maximum at about 266 nm, using the dissolution buffer as the blank.
For each of the tablets tested, calculate the total amount of Isoniazid (C6H7N3O) in the medium using the absorptivity value of 44.0 for isoniazid (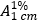 = 440). Evaluate the results as described under 5.5 Dissolution test for oral dosage forms, Acceptance criteria. The amount of Isoniazid released is not less than 80 % (Q) of the amount declared on the label.
= 440). Evaluate the results as described under 5.5 Dissolution test for oral dosage forms, Acceptance criteria. The amount of Isoniazid released is not less than 80 % (Q) of the amount declared on the label.
[Note from the Secretariat. The absorptivity value of isoniazid will be verified during the establishment of isoniazid ICRS.]
Impurity E (hydrazine). Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm).
As the mobile phase use a mixture of water R and acetonitrile R (40:60 V/V). Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 300 nm.
Prepare as a diluent a mixture of 50 volumes of water R and 50 volumes of acetonitrile R.
Prepare the following solutions freshly:
For solution (A), dilute 1 mL of benzaldehyde R to 50 mL with methanol R. Use this solution within 4 hours.
For solution (1), transfer a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 50.0 mg of Isoniazid, to a 50 mL volumetric flask. Suspend the powder in 1 mL of water R and mix with 5 mL of solution (A). Allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent.
For solution (2), transfer 20.0 mg of hydrazine sulfate R (equivalent to 4.925 mg of hydrazine) to a 50 mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in water R and dilute to volume with the same solvent. Dilute 2.5 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with water R. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 25 mL volumetric flask, add 2.5 mL of solution (A), mix and allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent. Dilute 15.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with the diluent.
For solution (3), transfer 1 mL of water R to a 25 mL volumetric flask, add 2.5 mL of solution (A), mix and allow to stand for 45 minutes. Then dilute to volume with the diluent. Dilute 15.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with the diluent.
Inject 10 µL each of solutions (1), (2) and (3) and record the chromatograms for about 30 minutes.
Use the chromatogram obtained with solutions (2) and (3) to identify the peak due to the reaction product of benzaldehyde and hydrazine, benzaldehyde azine (benzaldehyde azine is eluted at about 20 minutes). The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2), the signal-to-noise ratio of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine is at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to benzaldehyde azine is not greater than the area of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (15 ppm).
Related substances. Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated and end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
-
mobile phase A: a mixture of 0.5 volume of acetonitrile R and 100 volumes of ammonium formate buffer, pH 7.2;
-
mobile phase B: a mixture of 50 volumes of acetonitrile and 50 volumes of phosphate buffer pH 7.2.
Prepare the ammonium formate buffer by dissolving 0.315 g of ammonium formate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding ammonia (~10 g/L) TS and diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
Prepare the phosphate buffer pH 7.2 by dissolving 2.64 g of diammonium hydrogen phosphate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding phosphorous acid (~105 g/L) TS and diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
|
Time |
Mobile phase A |
Mobile phase B |
Comments |
|
0–9 |
99.5 |
0.5 |
Isocratic |
|
9–22 |
99.5 to 85 |
0.5 to 15 |
Linear gradient |
|
22-35 |
85 to 60 |
15 to 40 |
Linear gradient |
|
35-36 |
60 |
40 |
Isocratic |
|
36–37 |
60 to 99.5 |
40 to 0.5 |
Return to initial composition |
|
37–45 |
99.5 |
0.5 |
Re-equilibration |
Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 266 nm.
Prepare the following solutions freshly using mobile phase A as a diluent.
For solution (1), transfer a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 100 mg of Isoniazid, into a 100 mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of mobile phase A and sonicate for 10 minutes. Cool to room temperature, dilute to volume and filter. For solution (2), dilute 1.0 mL of solution (1) to 100.0 mL. For solution (3), dilute 5.0 mL of solution (2) to 50.0 mL. For solution (4), dissolve 5 mg of isonicotinic acid R (impurity A), 5 mg of isonicotinamide R (impurity B), 5 mg of nicotinoyl hydrazide R (impurity D), 5 mg of benzoyl hydrazide (impurity G), and 5 mg of 3,5-di(pyridin-4-yl)-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-amine R (impurity I) and dilute to 50.0 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with solution (1).
Inject 5 µL each of solutions (1), (2), (3) and (4).
Use the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) to identify the peaks due to the impurities A, B, D, G and I. The impurities are eluted, if present, at the following relative retention with reference to isoniazid (retention time about 11.7 minutes): impurity A about 0.32; impurity D about 1.15; impurity B about 1.30, impurity F about 1.59; impurity H about 1.98; impurity G about 2.05; impurity C about 2.11; impurity I about 2.38.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4), the peak-to-valley ratio (Hp/Hv) is at least 2.0, where Hp is the height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity D and Hv is the height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to isoniazid. Also, the test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the peak due to isoniazid is detected with a signal-to-noise ratio of at least 10.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.5, is not greater than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B, when multiplied by a correction factor of 1.4, is not greater than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity G, when multiplied with a correction factor of 2.6, is not greater than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2 %);
-
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity I, when multiplied with a correction factor of 0.33, is not greater than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2 %); and
-
the area of any other impurity peak is not greater than 0.2 times the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.2 %).
-
The sum of the areas of all impurity peaks, including the corrected areas of any peaks corresponding to impurities A, B, G and I, is not greater than the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0 %). Disregard any peaks with an area of less than the area of the peak due to isoniazid in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.1%).
Assay
-
Either method A or B may be applied.
-
Carry out the test as described under 1.14.1 Chromatography, High-performance liquid chromatography, using a stainless steel column (25 cm x 4.6 mm) packed with base-deactivated and end-capped particles of silica gel, the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm).
Use the following conditions for gradient elution:
-
mobile phase A: a mixture of 0.5 volume of acetonitrile R and 100 volumes of ammonium formate buffer, pH 7.2;
-
mobile phase B: a mixture of 50 volumes of acetonitrile R and 50 volumes of phosphate buffer pH 7.2.
Prepare the ammonium formate buffer by dissolving 0.315 g of ammonium formate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding ammonia (~10 g/L) TS and diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
Prepare the phosphate buffer pH 7.2 by dissolving 2.64 g of diammonium hydrogen phosphate R in 950 mL of water R, adjusting the pH to 7.2 by adding phosphorous acid (~105 g/L) TS and diluting to 1000 mL with water R.
Time
(minutes)Mobile phase A
(% V/V)Mobile phase B
(% V/V)Comments
0–10
100
0
Isocratic
10–18
100 to 25
0 to 75
Linear gradient
18-20
25
75
Isocratic
20-20.1
25 to 100
75 to 0
Return to initial composition
20.1-25
60 to 100
40 to 0
Re-equilibration
Operate with a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute. As a detector, use an ultraviolet spectrophotometer set at a wavelength of 266 nm.
Prepare the following solutions freshly in mobile phase A.
For solution (1), weigh and powder 20 tablets. Transfer a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 60.0 mg of Isoniazid, into a 200 mL volumetric flask. Add 80 mL of mobile phase A and sonicate for 10 minutes. Cool to room temperature, dilute to volume with mobile phase and filter.
For solution (2), dissolve 60 mg of isoniazid RS and dilute to 200.0 mL with mobile phase A.
Inject 5 µL each of solutions (1) and (2).
Measure the areas of the peaks corresponding to isoniazid obtained in the chromatograms of solutions (1) and (2) and calculate the percentage content of Isoniazid (C6H7N3O) in the tablets using the declared content of C6H7N3O in isoniazid RS.
-
-
Prepare as a diluent a solvent mixture of 80 volumes of ethanol R and 20 volumes of water R. Weigh and powder 20 tablets. Transfer a quantity of the powdered tablets, nominally containing 50.0 mg of isoniazid to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add about 50 mL of the diluent, sonicate for about 5 minutes, allow to cool to room temperature, and make up to volume with the diluent. Filter a portion of this solution, discarding the first few mL of the filtrate. Dilute 2.0 mL of the filtrate to 50.0 mL with the diluent.
Measure the absorbance as described under 1.6 Spectrophotometry in the visible and ultraviolet regions of the resulting solution in a cuvette or cell with an optical pathlength of 10 mm at the maximum at about 263 nm, using the solvent mixture as the blank. At the same time and under the same conditions, measure the absorbance of a solution of isoniazid RS with a suitable concentration in the diluent. Calculate the content of isoniazid (C6H7N3O) in the tablets from the results obtained.
[Note from the Secretariat : It is intended to determine the absorptivity value of isoniazid during the establishment of isoniazid RS and to use this value for the calculation of the assay result.]
Impurities
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed in the monograph on Isoniazid.